- Utility Menu

Harvard Natural Sciences Lecture Demonstrations
1 Oxford St Cambridge MA 02138 Science Center B-08A (617) 495-5824
- Key to Catalog
enter search criteria into the search box
Cavendish experiment.
Calculation of gravitational constant, with accompanying apparatus model.
What it shows
The gravitational attraction between lead spheres. The data from the demonstration can also be used to calculate the universal gravitational constant G.
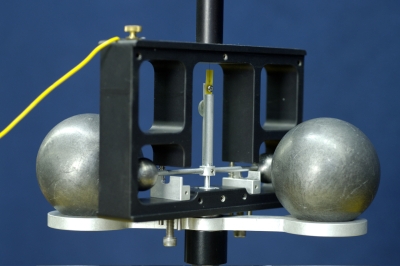

How it works
The Cavendish apparatus basically consists of two pairs of spheres, each pair forming dumbbells that have a common swivel axis ( figure 1). One dumbbell is suspended from a quartz fiber and is free to rotate by twisting the fiber; the amount of twist measured by the position of a reflected light spot from a mirror attached to the fiber. The second dumbbell can be swiveled so that each of its spheres is in close proximity to one of the spheres of the other dumbbell; the gravitational attraction between two sets of spheres twists the fiber, and it is the measure of this twist that allows the magnitude of the gravitational force to be calculated.
The Cavendish apparatus we currently use is built by PASCO. 1 The quartz fiber and smaller dumbbell are enclosed in a metal case with glass window for protection. A plan view of the spheres and dimensions are given in figure 2. A HeNe laser is used to provide the spot reflection. When the apparatus is used quantitatively, the swing-time method is usually employed to calculate G.
The large dumbbell is rotated on its axis so that the spheres press up against the glass shield next to the smaller spheres (see figure 2). The gravitational attraction between the spheres exerts a torque on the quartz fiber which twists through a small angle. The position of the reflected spot is noted and the large dumbbell is moved to its second position on the other side of the glass; gravitational attraction twists the fiber in the opposite direction. The response time of the spot to move to the second position and the final spot position are noted. The speed with which the fiber can respond to the move depends upon its torsional constant κ, which can be calculated by measuring the period of oscillation of the fiber,
The applied torque due to the gravitational attraction τ=κθ where θ is the maximum angle of deflection of the light spot. At this maximum deflection, the force between a large sphere and a small sphere is
where r is the distance between sphere centers. It is related to the torque by τ=F(L/2) where L is the length of the small dumbbell. So the gravitational constant can be calculated by
Note that, as the mirror turns through an angle θ, the reflected light moves through 2θ. So by reversing the dumbbell an angle of 4θ is measured.
Data for this particular apparatus are given in table 1.
table 1. Cavendish apparatus data
Setting it up:
This experiment uses a very sensitive apparatus that requires patience and finesse to properly set up. Consult the printout of the PASCO user manual in the blue "Cavendish Experiment" folder in the filing cabinet.
- First find a stable platform and place it in the lecture hall. Although the balance has feet that can be adjusted to make it level, for best results the platform should be reasonably level as well.
- The PASCO balance currently in use is very sensitive, so to protect against damaging the torsion ribbon during transit the apparatus should be carried gingerly into the lecture hall and placed onto the platform.
- Remove the front plate of the balance to expose the small dumbbell and the adjustable support arms that immobilize it during transit. Lower the support arms so that they do not interfere with the dumbbells. Adjust the feet so that the entire apparatus is level, and replace the front plate.
- Use the yellow wire to electrically ground the apparatus. Place the large masses in the "neutral" position so that they are perpendicular with the small masses inside.
- At this point the dumbbell is probably moving quite a bit within the case; as the balance settles down, set up the laser at the appropriate distance and angle for the audience.
- The dumbbell vibrations will usually dampen-out after about 20 minutes. For faster setup, the motions can be dampened by slowly raising and lowering the support arms. If after settling the dumbbell continues to change direction abruptly, this means that the torsional equilibrium of the ribbon has strayed too far from where it should be, and the ribbon needs to be "zeroed."
- To zero the balance, start by carefully loosening the thumbscrew sticking out of the top of the main shaft. Also near the top, the large round knob attached to the elastic belt is used to change the direction of the ribbon (notice that there is a fine and a coarse adjustment knob). Wait until the dumbbell has made its full excursion in the direction of the needed adjustment to minimize added oscillation. Carefully re-tighten the thumbscrew (not too tight) and dampen the vibrating dumbbell as necessary. Repeat until zeroed.
The apparatus was originally invented by the Rev. John Michell in 1795 to measure the density of the Earth, and was modified by Henry Cavendish in 1798 to measure G. In 1785 Coulomb used a similar apparatus to measure the electrostatic force between charged pith balls. Apart from the historical significance of the experiment, it's really neat to see that you can measure such an incredibly weak force using such a simple device.
In a lecture hall setting the Cavendish apparatus is too small for the audience to see its workings. A large scale model of the dumbbell and fiber components are a good idea to help explain what's going on. We have built such a model from wood and brass, with dumbbell arm lengths of 50cm and the small dumbbell hanging from a copper wire. The larger spheres, made of wood, have magnets enclosed and the smaller spheres, of Styrofoam, have steel ball bearings at their centers.
1. M.H.Shamos, Great Experiments in Physics , (Henry Holt & Co. New York 1959) p.75, contains Cavendish's original paper 2. R.E. Crandall, Am J Phys 54 , 367, 1983. 3. J.Cl. Dousse and C. Rheme, Am J Phys 55 , 706, 1987. 4. Y.T. Chen and A. Cook, Gravitational Experiments in the Laboratory , (Cambridge University Press, 1993). 5. C. A. Coulomb, Premiere Memoire sur l’electricite et le Magnetisme, Histoire de l’Academie Royale des Sciences, 569-577 (1785).
1 available from CENCO 33210C, and PASCO SE-9633
Demo Subjects
Newtonian Mechanics Fluid Mechanics Oscillations and Waves Electricity and Magnetism Light and Optics Quantum Physics and Relativity Thermal Physics Condensed Matter Astronomy and Astrophysics Geophysics Chemical Behavior of Matter Mathematical Topics
Key to Catalog Listings
Size : from small [S] (benchtop) to extra large [XL] (most of the hall) Setup Time : <10 min [t], 10-15 min [t+], >15 min [t++] /span> Rating : from good [★] to wow! [★★★★] or not rated [—]
Complete key to listings

IMAGES
VIDEO