- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
extemporaneous

Definition of extemporaneous
Did you know.
Extemporaneous , which comes from the Latin phrase ex tempore ("on the spur of the moment"), joined the English language sometime in the mid-17th century. The word impromptu , also from a Latin phrase ( in promptu , meaning "in readiness") soon followed. In general usage, extemporaneous and impromptu are used interchangeably to describe off-the-cuff remarks or speeches, but this is not the case when they are used in reference to the learned art of public speaking. Teachers of speech will tell you that an extemporaneous speech is one that has been thoroughly prepared and planned but not memorized, whereas an impromptu speech is one for which absolutely no preparations have been made.
- down and dirty
extemporary
- improvisational
- off-the-cuff
- spur-of-the-moment
- unconsidered
- unpremeditated
- unrehearsed
Examples of extemporaneous in a Sentence
Word history.
Late Latin extemporāneus "done on the spur of the moment" (from Latin ex tempore "on the spur of the moment, extempore " + -āneus, suffix forming adjectives from temporal adverbs) + -ous
Note: Regarding the suffix -āneus see the etymology and note at spontaneous .
1673, in the meaning defined at sense 1a(1)
Articles Related to extemporaneous

Challenging Words You Should Know Vol 2
It isn’t linguistic hubris if you can back it up
Get Word of the Day delivered to your inbox!
Dictionary Entries Near extemporaneous
extemporaneity
Cite this Entry
“Extemporaneous.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/extemporaneous. Accessed 23 Nov. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of extemporaneous, more from merriam-webster on extemporaneous.
Nglish: Translation of extemporaneous for Spanish Speakers
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
How to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), plural and possessive names: a guide, the difference between 'i.e.' and 'e.g.', why is '-ed' sometimes pronounced at the end of a word, what's the difference between 'fascism' and 'socialism', popular in wordplay, 8 words with fascinating histories, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, birds say the darndest things, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version), 10 scrabble words without any vowels, games & quizzes.

Oratory Club
Public Speaking Helpline
What Is An Extemporaneous Speech?
If you’ve ever wondered, “What is an extemporaneous speech?” you’re in the right place! In this article, we’ll dive into the exciting world of extemporaneous speaking and discover what makes it a unique and thrilling form of communication. So, buckle up and get ready for an adventure in public speaking that’s going to blow your socks off!
Picture this: you’re standing in front of a crowd, your heart pounding with anticipation. The spotlight is on you, and you have limited time to come up with a persuasive and cohesive speech on a given topic. That’s what an extemporaneous speech is all about! It’s a thrilling challenge that tests your ability to think on your feet and deliver a compelling message without the luxury of extensive preparation.
But don’t fret! Extensive preparation doesn’t mean you’re left hanging in the wind. In fact, extemporaneous speakers use a variety of skills, such as critical thinking, research, and organization, to craft their speeches on the spot. So, if you’re ready to unleash your inner orator and captivate audiences with your spontaneous wit and charm, let’s dive deeper into the world of extemporaneous speaking!

Table of Contents
Understanding Extemporaneous Speech: A Guide to Spontaneous Expression
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on extemporaneous speech! Whether you’re a seasoned public speaker or just starting out, understanding what an extemporaneous speech is and how to deliver one effectively is crucial. In this article, we will explore the definition of an extemporaneous speech, its components, benefits, and provide tips for delivering an impressive extemporaneous speech. So, let’s dive right in!
What is an Extemporaneous Speech?
An extemporaneous speech is a type of public speaking that requires speakers to present a well-researched and organized speech on a given topic without extensive preparation or a fully written script. Unlike a scripted speech, where every word is written beforehand and memorized, an extemporaneous speech allows speakers to use notes or prompts for guidance while delivering their presentation.
Extemporaneous speeches are commonly used in academic settings, such as debates, competitions, and classroom presentations. They test the speaker’s ability to think on their feet, organize their thoughts quickly, and deliver a coherent and persuasive argument or message. Extemporaneous speaking combines elements of impromptu speaking and prepared speeches, striking a balance between spontaneity and structure.
One of the key aspects of an extemporaneous speech is the delivery style. Speakers should aim to maintain a conversational tone, engage the audience, and connect with them authentically. While some level of preparation is allowed, the main goal of an extemporaneous speech is to demonstrate critical thinking skills, adaptability, and effective communication.
The Components of an Extemporaneous Speech
Before diving into the process of delivering an extemporaneous speech, let’s take a closer look at its essential components:
- Preparation: While an extemporaneous speech is not fully scripted, it still requires some level of preparation. Speakers should gather information on the given topic, research relevant data, and formulate key points or arguments. This step ensures that the speech is well-informed and coherent.
- Structure: An extemporaneous speech typically follows a basic structure, including an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should grab the audience’s attention, introduce the topic, and provide a clear thesis statement. The body should consist of main points supported by evidence, while the conclusion should summarize the key ideas and leave a lasting impression.
- Delivery: As mentioned earlier, the delivery of an extemporaneous speech should be conversational and engaging. Speakers should maintain eye contact with the audience, use appropriate gestures and body language, and speak clearly and confidently. It is important to strike a balance between sticking to the main points and allowing flexibility in responding to the audience’s reactions.
Tips for Delivering an Impressive Extemporaneous Speech
Now that we have a basic understanding of what an extemporaneous speech entails, let’s explore some tips for delivering an impressive extemporaneous speech :
- Practice active listening: Engage in active listening to absorb information and gather different perspectives on the given topic. This will enable you to develop a well-rounded and informed speech.
- Understand the audience: Consider the demographics, interests, and knowledge level of the audience. Tailor your speech to resonate with them and address their specific needs or concerns.
- Organize your thoughts: Utilize note-taking techniques, such as mind maps or bullet points, to organize your thoughts and maintain a clear structure during your speech.
- Practice improvisation: Embrace impromptu speaking opportunities to enhance your ability to think on your feet and respond to unexpected questions or challenges.
- Focus on body language: Pay attention to your body language, facial expressions, and vocal tone. Maintain a confident posture, make eye contact with the audience, and use gestures to emphasize your points.
- Engage the audience: Make your speech interactive by asking questions, incorporating storytelling, or inviting the audience to participate. This will create a dynamic and memorable experience.
- Reflect and learn: After delivering your extemporaneous speech, take the time to reflect on your performance. Identify areas for improvement, seek feedback from others, and continue refining your skills.
Benefits of Mastering Extemporaneous Speaking
Moving beyond the basics, let’s explore some of the benefits of mastering extemporaneous speaking :
1. Enhanced Communication Skills
Extemporaneous speaking hones your ability to articulate ideas clearly, engage with an audience, and adapt your message based on their reactions. This translates into improved communication skills that are valuable in various personal and professional scenarios.
2. Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
Delivering an extemporaneous speech requires quick thinking, analyzing information, and developing logical arguments on the spot. By regularly practicing this skill, you’ll strengthen your critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
3. Confidence Building
As you become more adept at delivering impromptu speeches, your self-confidence will grow. The ability to express yourself confidently and coherently in front of an audience can boost your self-esteem and positively impact other areas of your life.
Mastering Extemporaneous Speaking: A Lifelong Journey
Now that you have the knowledge and tips to deliver an impressive extemporaneous speech, it’s time to embark on your journey of mastering this valuable skill. Remember, extemporaneous speaking requires practice, patience, and a willingness to step out of your comfort zone. Embrace each speaking opportunity as a chance to grow and learn, and soon you’ll be captivating audiences with your well-crafted and spontaneous speeches. Happy speaking!
Key Takeaways: What is an Extemporaneous Speech?
- An extemporaneous speech is a speech that is delivered without extensive preparation.
- It allows the speaker to effectively communicate their ideas in a spontaneous and natural manner.
- This type of speech is commonly used in competitions or public speaking events.
- Key skills for delivering an extemporaneous speech include good organization, clear articulation, and the ability to think on your feet.
- Practicing and familiarizing yourself with different topics can help improve your extemporaneous speaking skills.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our frequently asked questions section where we’ll answer common inquiries about extemporaneous speeches. Whether you’re a student preparing for a school assignment or an aspiring public speaker, we’ve got you covered. Discover the ins and outs of extemporaneous speaking below.
1. How would you define an extemporaneous speech?
An extemporaneous speech is a type of impromptu presentation where the speaker delivers a prepared speech without relying on a script or memorized content. It requires the speaker to think on their feet and express their thoughts and ideas in a clear, concise, and organized manner. Rather than being fully spontaneous, an extemporaneous speech involves some level of preparation, research, and organization. This type of speaking encourages adaptability and quick thinking.
Extemporaneous speeches are often given in educational settings, competitions, or professional environments. They help develop skills such as critical thinking, effective communication, and the ability to convey complex ideas in a limited amount of time.
2. How does an extemporaneous speech differ from other types of speech?
An extemporaneous speech differs from other types of speeches, such as impromptu speeches, scripted speeches, or memorized speeches, in several ways. Unlike an impromptu speech, which is delivered with little to no preparation, an extemporaneous speech involves some level of prior research and organization. It allows speakers to gather information and structure their thoughts before stepping up to deliver their speech.
On the other hand, a scripted speech is one that is completely written out beforehand, while a memorized speech is fully memorized and recited word-for-word. In contrast, an extemporaneous speech requires the speaker to have a general idea of what they want to say but allows for flexibility and adaptation while delivering the speech.
3. What are the benefits of delivering an extemporaneous speech?
Delivering an extemporaneous speech offers several benefits. Firstly, it helps develop critical thinking skills as speakers must quickly analyze information and construct their arguments in a coherent manner. It also enhances public speaking skills by encouraging improvisation, adaptability, and engagement with the audience.
Extemporaneous speaking can also boost self-confidence as speakers learn to trust their knowledge and ability to convey ideas without relying on a script. Additionally, it helps improve research skills and the ability to synthesize information into a persuasive speech. Overall, the benefits of delivering an extemporaneous speech extend beyond the realm of public speaking and can be applied to various areas of personal and professional development.
4. What are some tips for delivering an effective extemporaneous speech?
To deliver an effective extemporaneous speech, it’s essential to focus on a few key tips. Firstly, practice impromptu speaking regularly to develop quick thinking and organization skills. Additionally, familiarize yourself with current events and gather knowledge on various topics to have a broader pool of information to draw from during your speech.
When delivering the speech, maintain eye contact with the audience, use confident body language, and vary your tone and pace to keep the listeners engaged. Structure your speech with a clear introduction, main points, and a concise conclusion. Finally, practice time management to ensure your speech fits within the allotted timeframe.
5. Can anyone become proficient in delivering extemporaneous speeches?
Absolutely! With practice and perseverance, anyone can become proficient in delivering extemporaneous speeches. The key is to start by gradually building your skills. Begin by practicing impromptu speaking in a supportive environment with friends or family members. As you gain confidence, challenge yourself by participating in public speaking events or competitions where you can receive constructive feedback.
Engage in activities that enhance critical thinking, such as reading extensively and staying informed about current events. Seek opportunities to speak in front of others, whether it’s in school, community events, or professional settings. Remember, becoming proficient in extemporaneous speaking is a journey that requires patience and a willingness to learn from both successes and failures.
How to Deliver an Extemporaneous Presentation or Speech
So, now you know what an extemporaneous speech is! It’s a speech you make without a script or memorizing everything. You get a topic and a little time to prepare, and then you speak from what you already know. It’s a great way to practice thinking on your feet and sharing your ideas with others. Just remember to stay calm, be confident, and have fun with it!
In an extemporaneous speech, you need to organize your thoughts, use examples to support your ideas, and speak clearly and confidently. Don’t stress too much about being perfect – the important thing is to connect with your audience and share your knowledge. So next time you have to give an extemporaneous speech, remember the tips and techniques we’ve discussed, and go out there and shine!
Similar Posts

Best Public Speaking Coaches
The best public speaking coaches are highly skilled professionals who help individuals improve their communication and presentation skills. With their expertise and guidance, they can assist in building confidence, enhancing delivery techniques, and refining content to ensure impactful and effective speeches. Personalized coaching sessions tailored to individual needs and goals are key to their success…
Which Jobs Require Public Speaking?
Public speaking is required in jobs such as sales, teaching, broadcasting, and politics. These professions often involve presenting information to an audience, and effective communication skills are critical for success. Whether it’s delivering a persuasive sales pitch, imparting knowledge to students, reporting news on live television, or engaging with the public as a political figure,…

How to Sell Powerpoint Presentations Online?
To sell PowerPoint presentations online, create a professional website and showcase your work through high-quality images and informative descriptions. Then, optimize your website for search engines by incorporating relevant keywords into your content and meta tags. Additionally, leverage social media platforms and online marketplaces to expand your reach and drive traffic to your website. Offer…

Ways to Practice Public Speaking
Practice public speaking by joining a Toastmasters club or taking a public speaking course. Learning and practicing in a supportive environment can help improve your skills and build confidence. In addition, you can practice by recording yourself speaking and reviewing the playback to identify areas for improvement. Regularly challenging yourself to speak in front of…

What are the Benefits of Speaking Properly in Business?
Speaking properly in business provides numerous benefits, such as enhancing communication effectiveness and creating a positive impression on clients and colleagues. It enables clear and concise message delivery, ensuring understanding and preventing miscommunication. Proper speech also promotes professionalism, credibility, and confidence, establishing trust and strong relationships in the business environment. When language is articulated well,…
NEVER Face Anxiety During a Speech (5 Formulas)
Public speaking anxiety is a challenge that many face—even seasoned speakers! The fear of a quivering voice, shaky hands, or a blank mind can make any speaking opportunity feel overwhelming. But what if there were practical methods to conquer that fear? Here are five easy and effective strategies to ensure that you never have to…

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
14.1 Four Methods of Delivery
Learning objectives.
- Differentiate among the four methods of speech delivery.
- Understand when to use each of the four methods of speech delivery.

Maryland GovPics – House of Ruth Luncheon – CC BY 2.0.
The easiest approach to speech delivery is not always the best. Substantial work goes into the careful preparation of an interesting and ethical message, so it is understandable that students may have the impulse to avoid “messing it up” by simply reading it word for word. But students who do this miss out on one of the major reasons for studying public speaking: to learn ways to “connect” with one’s audience and to increase one’s confidence in doing so. You already know how to read, and you already know how to talk. But public speaking is neither reading nor talking.
Speaking in public has more formality than talking. During a speech, you should present yourself professionally. This doesn’t mean you must wear a suit or “dress up” (unless your instructor asks you to), but it does mean making yourself presentable by being well groomed and wearing clean, appropriate clothes. It also means being prepared to use language correctly and appropriately for the audience and the topic, to make eye contact with your audience, and to look like you know your topic very well.
While speaking has more formality than talking, it has less formality than reading. Speaking allows for meaningful pauses, eye contact, small changes in word order, and vocal emphasis. Reading is a more or less exact replication of words on paper without the use of any nonverbal interpretation. Speaking, as you will realize if you think about excellent speakers you have seen and heard, provides a more animated message.
The next sections introduce four methods of delivery that can help you balance between too much and too little formality when giving a public speech.
Impromptu Speaking
Impromptu speaking is the presentation of a short message without advance preparation. Impromptu speeches often occur when someone is asked to “say a few words” or give a toast on a special occasion. You have probably done impromptu speaking many times in informal, conversational settings. Self-introductions in group settings are examples of impromptu speaking: “Hi, my name is Steve, and I’m a volunteer with the Homes for the Brave program.” Another example of impromptu speaking occurs when you answer a question such as, “What did you think of the documentary?”
The advantage of this kind of speaking is that it’s spontaneous and responsive in an animated group context. The disadvantage is that the speaker is given little or no time to contemplate the central theme of his or her message. As a result, the message may be disorganized and difficult for listeners to follow.
Here is a step-by-step guide that may be useful if you are called upon to give an impromptu speech in public.
- Take a moment to collect your thoughts and plan the main point you want to make.
- Thank the person for inviting you to speak.
- Deliver your message, making your main point as briefly as you can while still covering it adequately and at a pace your listeners can follow.
- Thank the person again for the opportunity to speak.
- Stop talking.
As you can see, impromptu speeches are generally most successful when they are brief and focus on a single point.
Extemporaneous Speaking
Extemporaneous speaking is the presentation of a carefully planned and rehearsed speech, spoken in a conversational manner using brief notes. By using notes rather than a full manuscript, the extemporaneous speaker can establish and maintain eye contact with the audience and assess how well they are understanding the speech as it progresses. The opportunity to assess is also an opportunity to restate more clearly any idea or concept that the audience seems to have trouble grasping.
For instance, suppose you are speaking about workplace safety and you use the term “sleep deprivation.” If you notice your audience’s eyes glazing over, this might not be a result of their own sleep deprivation, but rather an indication of their uncertainty about what you mean. If this happens, you can add a short explanation; for example, “sleep deprivation is sleep loss serious enough to threaten one’s cognition, hand-to-eye coordination, judgment, and emotional health.” You might also (or instead) provide a concrete example to illustrate the idea. Then you can resume your message, having clarified an important concept.
Speaking extemporaneously has some advantages. It promotes the likelihood that you, the speaker, will be perceived as knowledgeable and credible. In addition, your audience is likely to pay better attention to the message because it is engaging both verbally and nonverbally. The disadvantage of extemporaneous speaking is that it requires a great deal of preparation for both the verbal and the nonverbal components of the speech. Adequate preparation cannot be achieved the day before you’re scheduled to speak.
Because extemporaneous speaking is the style used in the great majority of public speaking situations, most of the information in this chapter is targeted to this kind of speaking.
Speaking from a Manuscript
Manuscript speaking is the word-for-word iteration of a written message. In a manuscript speech, the speaker maintains his or her attention on the printed page except when using visual aids.
The advantage to reading from a manuscript is the exact repetition of original words. As we mentioned at the beginning of this chapter, in some circumstances this can be extremely important. For example, reading a statement about your organization’s legal responsibilities to customers may require that the original words be exact. In reading one word at a time, in order, the only errors would typically be mispronunciation of a word or stumbling over complex sentence structure.
However, there are costs involved in manuscript speaking. First, it’s typically an uninteresting way to present. Unless the speaker has rehearsed the reading as a complete performance animated with vocal expression and gestures (as poets do in a poetry slam and actors do in a reader’s theater), the presentation tends to be dull. Keeping one’s eyes glued to the script precludes eye contact with the audience. For this kind of “straight” manuscript speech to hold audience attention, the audience must be already interested in the message before the delivery begins.
It is worth noting that professional speakers, actors, news reporters, and politicians often read from an autocue device, such as a TelePrompTer, especially when appearing on television, where eye contact with the camera is crucial. With practice, a speaker can achieve a conversational tone and give the impression of speaking extemporaneously while using an autocue device. However, success in this medium depends on two factors: (1) the speaker is already an accomplished public speaker who has learned to use a conversational tone while delivering a prepared script, and (2) the speech is written in a style that sounds conversational.
Speaking from Memory
Memorized speaking is the rote recitation of a written message that the speaker has committed to memory. Actors, of course, recite from memory whenever they perform from a script in a stage play, television program, or movie scene. When it comes to speeches, memorization can be useful when the message needs to be exact and the speaker doesn’t want to be confined by notes.
The advantage to memorization is that it enables the speaker to maintain eye contact with the audience throughout the speech. Being free of notes means that you can move freely around the stage and use your hands to make gestures. If your speech uses visual aids, this freedom is even more of an advantage. However, there are some real and potential costs. First, unless you also plan and memorize every vocal cue (the subtle but meaningful variations in speech delivery, which can include the use of pitch, tone, volume, and pace), gesture, and facial expression, your presentation will be flat and uninteresting, and even the most fascinating topic will suffer. You might end up speaking in a monotone or a sing-song repetitive delivery pattern. You might also present your speech in a rapid “machine-gun” style that fails to emphasize the most important points. Second, if you lose your place and start trying to ad lib, the contrast in your style of delivery will alert your audience that something is wrong. More frighteningly, if you go completely blank during the presentation, it will be extremely difficult to find your place and keep going.
Key Takeaways
- There are four main kinds of speech delivery: impromptu, extemporaneous, manuscript, and memorized.
- Impromptu speaking involves delivering a message on the spur of the moment, as when someone is asked to “say a few words.”
- Extemporaneous speaking consists of delivering a speech in a conversational fashion using notes. This is the style most speeches call for.
- Manuscript speaking consists of reading a fully scripted speech. It is useful when a message needs to be delivered in precise words.
- Memorized speaking consists of reciting a scripted speech from memory. Memorization allows the speaker to be free of notes.
- Find a short newspaper story. Read it out loud to a classroom partner. Then, using only one notecard, tell the classroom partner in your own words what the story said. Listen to your partner’s observations about the differences in your delivery.
- In a group of four or five students, ask each student to give a one-minute impromptu speech answering the question, “What is the most important personal quality for academic success?”
- Watch the evening news. Observe the differences between news anchors using a TelePrompTer and interviewees who are using no notes of any kind. What differences do you observe?
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- College Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Expository Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Scholarship Essay
- Admission Essay
- Reflective Essay
- Nursing Essay
- Economics Essay
Assignments
- Term Papers
- Research Papers
- Case Studies
- Dissertation
- Presentation
- Editing Help
- Cheap Essay Writing
- How to Order
Speech Writing
Extemporaneous Speech
How to Write an Extemporaneous Speech? A Step-by-Step Guide

People also read
The 10 Key Steps for Perfect Speech Writing
Understanding Speech Format - Simple Steps for Outlining
How to Start A Speech - 13 Interesting Ideas & Examples
20+ Outstanding Speech Examples for Your Help
Common Types of Speeches that Every Speechwriter Should Know
Good Impromptu Speech Topics for Students
Entertaining Speech Topics for Your Next Debate
Understanding Special Occasion Speech: Types, Steps, Examples and Tips
Introduction Speech- Tips & Examples
How to Write A Good Acceptance Speech?
Writing A Presentation Speech In English: Tips And Examples
Commemorative Speech - Writing Guide, Outline & Examples
Farewell Speech | Writing Tips & Examples
A Graduation Speech Writing Guide with Examples
Do you have to give an extemporaneous speech but don't know where to start? You're in the right place!
Whether you're a student in a debate or a professional giving an impromptu speech, this guide will help you craft a great speech. We'll explain what an extemporaneous speech is, give you examples, and share some tips to help you understand the topic better.
This step-by-step guide will help you write a fantastic extemporaneous speech that will captivate your audience.
So, let's get started!
- 1. Understanding Extemporaneous Speech
- 2. 7 Easy Steps to Writing an Extemporaneous Speech
- 3. Extemporaneous Speech Examples
- 4. Extemporaneous Speech Topics
- 5. Tips for Improving Extemporaneous Speech Delivery

Understanding Extemporaneous Speech
An extemporaneous speech is a type of speech delivered with little to no preparation, often with the help of notes or an outline. Unlike a memorized or read speech, an extemporaneous speech allows for more natural delivery and interaction with the audience, as the speaker can adapt to the audience's reactions and feedback in real-time.
This style of speech writing is commonly used in debates, public speaking events, and professional presentations.
An example of an extemporaneous speech situation is when a student is asked to give an impromptu talk on a current news headline in front of the class. Note that, unlike manuscript speeches, extemporaneous speeches are not read word-for-word from a prepared script. They allow for more flexibility and spontaneity in delivery.
Comparing Impromptu and Extemporaneous Speech
The above extemporaneous speech definition might make you think that impromptu and extemporaneous speech sound similar. But that is not the case.
Let’s take a look at the key difference between the two speech types:
- Impromptu speeches do not allow preparation for the speech and they often lack structure and familiarity.
- On the other hand, extemporaneous speeches require a little preparation time, some organization, and familiar topics.
Let’s take a look at some of the advantages and disadvantages of extemporaneous speech.
Advantages of Extemporaneous Speech
- Enhanced Communication Skills: Improves public speaking, listening, and interpersonal communication skills.
- Confidence Boost: Regular practice instills self-assurance in various speaking situations.
- Adaptability: Speakers learn to tailor their message to the interests and concerns of different audiences.
- Quick Thinking: Extemporaneous speaking sharpens the ability to think quickly and make decisions on the spot.
Disadvantages of Extemporaneous Speech
- Lack of Preparation: Speakers may deliver incomplete or less coherent presentations due to limited preparation.
- Potential for Inaccuracy: The absence of time for thorough research can lead to providing inaccurate information.
- Nervousness: The pressure of impromptu speaking can lead to anxiety and reduced confidence.
- Time Constraints: Speakers must manage their time effectively to stay within the allotted timeframes, adding to the pressure.
7 Easy Steps to Writing an Extemporaneous Speech
Let’s take a look at some easy steps to writing an extemporaneous speech that you can follow along:
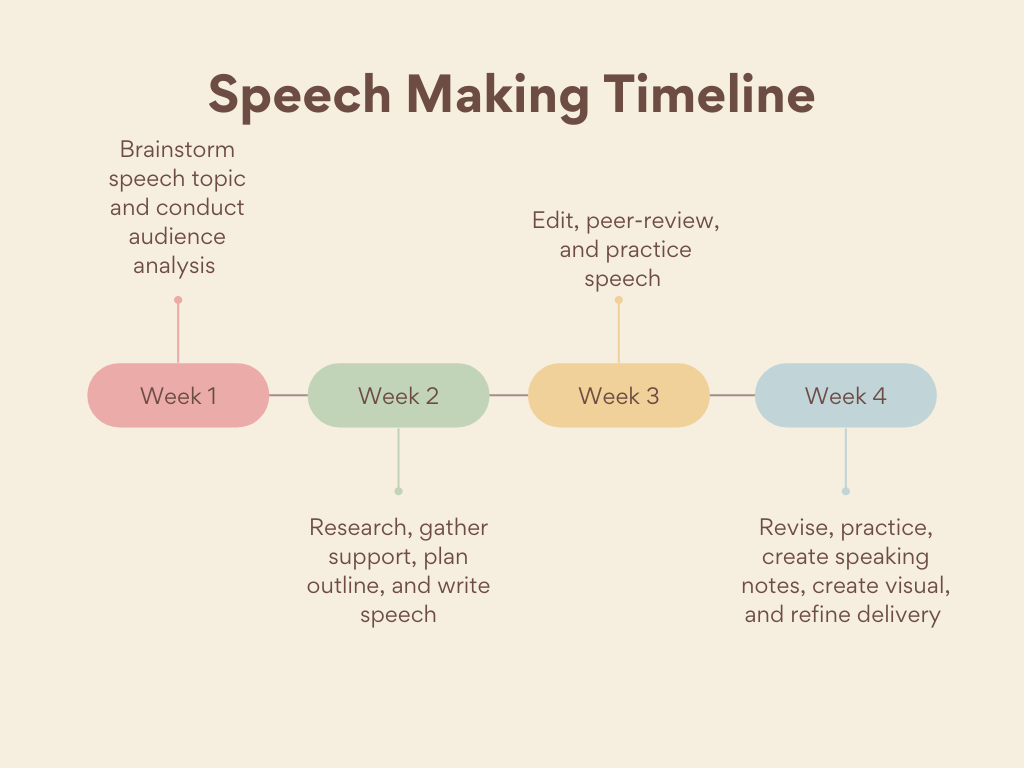
Step 1 - Research and Gather Information
To write a compelling extemporaneous speech, you must gather relevant information quickly. This step includes:
- Identifying the Topic or Prompt: Understand the subject or question you'll be speaking about.
- Finding Reliable Sources: Utilize trustworthy resources to gather facts, statistics, and arguments.
Step 2 - Create an Extemporaneous Speech Outline
An outline will give you a basic blueprint of the speech and can even help you weed out any potential mistakes in the speech format .
Though the speech outline can vary depending on the type of speech you are writing, here is an extemporaneous speech format you can follow:
Step 3 - Crafting a Strong Introduction
It is crucial to capture your audience's attention in the introduction and set the tone for your message.
Here is what you need to keep in mind when writing the introduction ;
- Use an attention-grabbing technique to engage your listeners.
- Formulate a clear and concise thesis statement that clearly states the main point of your speech.
- Explain why the topic is relevant or important.
Step 4 - Developing Compelling Main Points
The main body of your speech should convey your message effectively and coherently. Here are the things you should keep in mind;
- Identify key ideas and supporting details to determine the main arguments. If possible, try to gather and mention any evidence to back up your arguments.
- Make sure that your speech flows logically and smoothly.
- Use real-life examples, personal stories, and relevant statistics to make your points more compelling and understandable.
Step 5 - Engaging the Audience
Engaging your audience is essential for an effective extemporaneous speech. You can achieve that by maintaining your body language to establish a connection with your listeners.
You should also develop the audience's interests by tailoring your speech to address their concerns and interests.
Step 6 - Handling Transitions
Transitions are essential for keeping your speech coherent and organized. This step includes:
- Make sure your ideas flow seamlessly in the speech, creating a natural progression.
- Use words and phrases that act as guideposts for your audience through your speech.
- Avoid sudden changes in the topic that could leave your listeners confused.
Step 7 - Navigating the Conclusion
Concluding your speech effectively leaves a lasting impression. Here is what you should keep in mind when writing:
- Recap key points to ensure your audience leaves with a clear understanding of your main arguments.
- Make your message resonate with your listeners by delivering a powerful closing statement.
- Invite questions or comments from your audience to engage them.
Extemporaneous Speech Examples
Let’s take a look at an example of an extemporaneous speech situation:
The above example of extemporaneous speech addresses the topic of the impact of social media on modern society. It provides a well-structured, balanced, and informative discussion of the subject while maintaining a clear and engaging delivery style.
Here are some more extemporaneous speech samples to let you have a better understanding of how to write a speech;
Extemporaneous Speech Example
Extemporaneous Speech Example for Students
Extemporaneous Speech Example About Life
Extemporaneous Speech Example About Education
Be sure to check out more speech examples to have a better understanding of structuring and formatting a speech.
Extemporaneous Speech Topics
Here are some ideas for extemporaneous speech that you can use for practice or in various speaking situations:
- The impact of urban farming on local food security
- The role of virtual influencers in shaping consumer behavior
- The potential of biohacking for personal health optimization
- The influence of ancient philosophy on modern leadership styles
- The implications of space tourism for global economies
- The resurgence of vinyl records in the digital age
- The effect of minimalism on consumer culture and sustainability
- The role of augmented reality in enhancing historical site tours
- The cultural significance of traditional tattoos in contemporary society
- The ethical considerations of using AI in criminal justice systems
Be sure to check out more speech topics to select the one that stands out to you the most.
Tips for Improving Extemporaneous Speech Delivery
Here are some extemporaneous speech tips you can use to improve the delivery of your speech:
- Know Your Topic: Start by having a solid understanding of your topic. The more you know, the more confident you'll feel when speaking.
- Speak Clearly and Slowly: Pronounce your words clearly and speak at a moderate pace. Avoid rushing through your speech.
- Be Mindful of Fillers: Avoid using fillers such as "um," "uh," or "like." Practice eliminating these from your speech.
- Manage Nervousness: Nervousness is natural. Practice relaxation techniques, like deep breathing, before speaking to manage anxiety.
- Gestures and Body Language: Use appropriate gestures and body language to emphasize points and maintain audience interest.
- Eye Contact: Maintain eye contact with your audience. This creates a sense of connection and engagement.
- Vocal Variety: Vary your tone, pitch, and volume to keep your audience engaged. Avoid speaking in a monotone voice.
So there you have it!
Learning the art of writing an extemporaneous speech is a valuable skill that can benefit you in various personal and professional situations.
By following this step-by-step guide, practicing, and learning from your experiences, you can become a confident and effective extemporaneous speaker.
If you find yourself wondering, " Can I pay someone to do my essay ?"—we've got you covered. Our custom writing service can help you craft the perfect speech or any other written material you need.
The professional writers at MyPerfectWords.com are ready to partner with you to create an awesome public speaking experience.
So, buy speech today and let us help you shine!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the idea of extemporaneous speech.
The idea of extemporaneous speech is to deliver a well-organized and spontaneous presentation using minimal notes. It allows speakers to engage with their audience while showcasing their knowledge and ability to think on their feet.
What are the rules for extemporaneous speaking?
Some basic rules for extemporaneous speaking include:
- Stay on topic.
- Use clear and concise language.
- Maintain eye contact with the audience.
- Organize your thoughts logically.
- Avoid excessive filler words like "um" and "uh."
What are the characteristics of extemporaneous speaking?
Extemporaneous speaking is characterized by:
- Preparation with brief notes or an outline.
- Spontaneous delivery with natural language.
- Audience engagement and interaction.
- Adaptability to time constraints and audience feedback.
What techniques are used in extemporaneous speaking?
Techniques in extemporaneous speaking include:
- Mindful breathing to stay calm.
- Pausing for emphasis and clarity.
- Using gestures and body language effectively.
- Structuring your speech for clarity and impact.
What is the function of extemporaneous speaking?
The function of extemporaneous speaking is to inform, persuade, or entertain an audience with a well-prepared yet spontaneous presentation. It's often used to engage listeners in discussions, debates, or educational settings.
When would you use an extemporaneous speech?
Extemporaneous speech is widely used in academic, competitive, or professional settings. Speakers deliver presentations or arguments with minimal preparation, such as in debates, school presentations, and business meetings. This approach enables natural audience engagement and real-time adjustments based on feedback, making it valuable for dynamic and interactive speaking engagements.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.
Struggling With Your Paper?
Get a custom paper written at
With a FREE Turnitin report, and a 100% money-back guarantee
LIMITED TIME ONLY!
Keep reading

OFFER EXPIRES SOON!
All Subjects
Intro to Public Speaking
Study guides for every class, that actually explain what's on your next test, extemporaneous speech, from class:.
Extemporaneous speech is a type of public speaking that combines elements of preparation and spontaneity, allowing the speaker to deliver a speech with limited notes while maintaining a conversational tone. This approach encourages speakers to be flexible and responsive to their audience, enhancing engagement and connection. It's often used in contexts like debates, interviews, or situations where speakers need to present information quickly yet effectively.
congrats on reading the definition of Extemporaneous Speech . now let's actually learn it.
5 Must Know Facts For Your Next Test
- Extemporaneous speeches typically require a speaker to prepare key points and practice their delivery while remaining flexible for audience interaction.
- This style encourages a more natural and conversational approach, allowing the speaker to connect with the audience on a personal level.
- Speakers often use brief notes or outlines as prompts rather than reading from a full script, which helps maintain eye contact and engagement.
- Extemporaneous speaking is highly valued in competitive speaking events, such as forensics tournaments or public speaking contests, where adaptability is crucial.
- Mastering extemporaneous speech can enhance critical thinking skills as speakers learn to articulate thoughts clearly and respond to unexpected questions.
Review Questions
- Extemporaneous speech differs from impromptu speaking mainly in its level of preparation. While impromptu speeches are delivered spontaneously without any prior notice or preparation, extemporaneous speeches allow for some level of planning and organization. Speakers using the extemporaneous style typically prepare key points in advance and may use brief notes during their delivery. This approach enables them to be flexible and adapt to audience reactions while maintaining a structured presentation.
- The advantages of using extemporaneous speech include increased audience engagement and a more natural delivery. By relying on key points rather than a full script, speakers can maintain eye contact and interact more dynamically with their audience. This style allows for spontaneity, helping speakers to respond effectively to questions or comments from the audience. Additionally, the flexibility of extemporaneous speaking can lead to more authentic presentations, as speakers are able to convey their message in a conversational manner.
- Mastering extemporaneous speech requires several essential skills, including critical thinking, quick decision-making, and adaptability. These skills enable speakers to formulate clear thoughts rapidly and adjust their presentations based on audience feedback or questions. Strong organizational abilities are also crucial, as they help speakers develop coherent outlines that guide their delivery while allowing flexibility. Ultimately, these skills contribute significantly to effective public speaking by fostering confidence and enhancing the speaker's ability to connect with their audience in real-time.
Related terms
Impromptu Speaking : Impromptu speaking involves delivering a speech without prior preparation or notice, requiring quick thinking and adaptability.
Preparation Outline : A preparation outline is a structured plan that helps speakers organize their thoughts and key points before delivering a speech.
Delivery Techniques : Delivery techniques encompass various methods used by speakers to present their message effectively, including vocal variety, body language, and eye contact.
" Extemporaneous Speech " also found in:
Subjects ( 1 ).
- Writing for Public Relations
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
Ap® and sat® are trademarks registered by the college board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website..
- All Insights
- Top-Rated Articles
- How-to Guides
- For Parents
The Art of Extemporaneous Speech

Extemporaneous Speech
Have you ever been asked to give a speech or presentation without any prior notice or time to prepare? You're not alone. This is commonly referred to as an extemporaneous speech and it can happen in school, job interviews, and even in social settings. Extemporaneous speeches can be nerve-racking, but with some practice and understanding of the basics, you can deliver a great extemporaneous speech with ease. In this blog post, we'll explain what an extemporaneous speech is, why it's important, and how to do it.
What is an Extemporaneous Speech?
An extemporaneous speech is an impromptu speech that is given without any prior preparation. This means that you won't have any notes or a prepared written speech to read from. Instead, you will be expected to deliver a speech on a given topic on the spot. Extemporaneous speeches are commonly used in settings like debates, interviews, and public speaking competitions.
Why is it Important? Extemporaneous speeches are necessary in various situations, and the ability to deliver them effectively can be a valuable skill. They can help you communicate your thoughts and ideas in a concise and clear way , improve your critical thinking skills, and boost your confidence. Additionally, extemporaneous speeches can show that you are adaptable and can handle unexpected situations, which is a highly valued trait in many fields.
How to Deliver a Great Extemporaneous Speech?
Let's take a look at 8 important steps to making a great extemp speech:
Take a deep breath and stay calm.
This step is crucial in delivering a successful extemporaneous speech. When you are caught off-guard with a sudden request to speak, it can be easy to panic and feel overwhelmed. However, taking a deep breath and calming yourself down can help you to focus and gather your thoughts. Remember that it's okay to take a few seconds to compose yourself before beginning your speech. By doing so, you'll be able to deliver a more polished and confident performance. So, take a deep breath, relax your shoulders, and let your mind clear. You've got this!
Remember that confidence is key.
Don't be afraid to speak up and project your voice so that everyone in the audience can hear you. This doesn't mean you have to yell, but rather speak with conviction and clarity. By doing so, you'll capture the attention of your audience and keep them engaged throughout your speech. Remember, you're the one in control and the audience is there to listen to what you have to say. So, take a deep breath, stand up straight, and let your voice be heard.
Open Strong
Starting your extemporaneous speech with a strong opening statement is crucial in grabbing the audience's attention and setting the tone for the rest of your speech. You can start with a bold statement that challenges the audience's perspective or a rhetorical question that makes them think. Another way to begin is by sharing a personal anecdote or a relevant statistic that highlights the importance of the topic you will be addressing. It's essential to be creative and engaging in your opening statement to hook the audience from the get-go. Remember, the first few seconds of your speech can make or break your overall performance, so make them count!
Organize Your Thoughts
Organizing your thoughts is a crucial step in delivering a successful extemporaneous speech. Before you begin speaking, take a few seconds to collect your thoughts and ideas. This will help you to avoid rambling and keep your speech focused and concise. You can do this by taking a deep breath and mentally outlining your key points. Think about what you want to say and how you want to say it. Consider the order in which you want to present your ideas, and make sure that each point flows smoothly into the next. By taking the time to organize your thoughts, you'll be able to deliver a more polished and effective extemporaneous speech.
Use Simple Language
When giving an extemporaneous speech, it's important to remember that your audience may not be familiar with technical jargon or industry-specific acronyms. Using simple and accessible language can help ensure that your message is effectively communicated and understood by everyone in the room. Avoid using words that might confuse your audience and instead opt for clear and concise language that effectively conveys your ideas. This will not only make your speech easier to understand but also help to establish a connection with your audience, making them more receptive to your message.
Keep it Concise
When giving an extemporaneous speech, it's important to remember that time may be limited, and you need to make the most of it. Keeping your speech concise and to the point is crucial in delivering a successful speech. Start by answering the question fully, ensuring that you address all the key points. Avoid going off on tangents or rambling, as this can cause your audience to lose interest. Instead, focus on the main ideas and use concrete examples to illustrate your points. Remember, less is often more when it comes to extemporaneous speeches, so keep it simple and straightforward. By doing so, you'll be able to deliver a clear and effective speech that leaves a lasting impression on your audience.
Stick to the Time
Try to stick to the time limit if you have one. Going over the allotted time can not only annoy your audience, but it can also make it seem like you haven't organized your thoughts or prepared adequately. If you find that you have more to say than the time allows, consider focusing on the most important points and leaving out any tangents or less crucial information. Remember, being respectful of the time given to you shows that you are considerate of your audience's time and that you can effectively communicate your ideas within a given timeframe.
Finish Strong
End with a memorable closing statement that leaves a lasting impression on your audience. You can summarize your main points, provide a call to action, or leave the audience with a thought-provoking question. Another effective way to close your speech is by using a memorable quote or anecdote that ties back to your opening statement. Whatever method you choose, make sure that your closing is clear and concise, and that it effectively reinforces the main message of your speech. By ending with a strong and memorable closing statement, you'll leave your audience with a positive and lasting impression, and ensure that your message sticks with them long after you've finished speaking.
Delivering an extemporaneous speech can be challenging, but it is a valuable skill to have. It's important to understand what an extemporaneous speech is and why it is important. Hopefully, this blog post has provided you with some tips and tricks to help you deliver a great extemporaneous speech. Remember that practice makes perfect, so don't be afraid to practice your speaking skills whenever you can. Now go out there and show off your extemporaneous speaking skills!

Related Insights
How to incorporate humor in your speech: use appropriate tones (part 2), the art of persuasion: writing a compelling speech, using stage movements and gestures as foundations of persuasion: learn these 3 ways (part 2).

- 5 Prep Tips for BP
- Top Speech Introductions
- Public Speaking and Debate Competitions
- Incorporating Humor
- Logical Fallacies
- How-To: Prepare for Debate Tournaments
- How-To: Judge a Debate
- How-To: Win a BP Debate
- How-To: Win An Argument
- How-To: Improve at Home
- Team China Wins World Championship
- Ariel Wins Tournament
- Jaxon Speaks Up
- Tina Improves
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Download Free PDF
Extemporaneous Speeches: Definition and Delivery

Brief: Because extemporaneous speeches are not read or memorized, the extemporaneous speaker needs to stay in the moment and be able to "think on their feet"¾a process that can be stressful, but can also allow for a high level of spontaneity, leading to a natural, conversational style. Learning Objective: Demonstrate how to deliver an extemporaneous speech.
Related papers
Technical Communication Quarterly, 1998
Intra, 2022
54 famous public speeches from the past 150 years, from Abraham Lincoln to Volodymyr Zelenskyy and Charles III Can rhetoric make history? Yes, rhetoric has made it possible to enhance some extraordinary moments in history, or even to make some moments memorable precisely because of the use of words. This selection includes 54 famous public speeches from the past 150 years, listed in alphabetical order according to their authors. They range from the political speeches of Abraham Lincoln to those of Churchill, Blair and Obama, as well as Roosevelt and Kennedy, and ending with Elizabeth II and Charles III. However, also great speeches on civic issues are mentioned: from Martin Luther King Jr. to Nelson Mandela, from Jose Mujica Cordano to Sidney Poitier and Greta Thunberg. Moreover, some Nobel Prize acceptance speeches: from Ernest Hemingway to William Faulkner and Gabriel García Márquez, from John Steinbeck to Elie Wiesel and Malala Yousafzai. There is also one of the most famous motivational speeches ever, that of Steve Jobs, and the speeches of figures who also ruled history through words, such as Hitler and Mussolini. https://edizioni.intra.pro/prodotto/gianluca-sposito-great-speeches-the-art-of-public-speaking/
Extemporaneous speech is one of the main natural forms of public speaking, exercising students to speak in public with little preparation. Many English as Foreign Language (EFL) learners, especially those at Al-Quds Open University have difficulty to speak spontaneously in front of the public due to their inability to speak, rooting from their lack of speaking proficiency. Due to the students’ lack of competence in extemporaneous speech, the researcher aimed to investigate the English language undergraduates’ engagement in an extemporaneous speech at the English Language and Literature Department of the university. The researcher employed the qualitative approach to gain profound knowledge and understanding of the research problem. The researcher selected a purposive sampling to collect and analyze the required data for efficient usage of the resources. The observation was performed on a selected class of ‘Language Use’ course, consisted of 35 students, at the English language and L...
Robert Frost, the great romantic poet avers that, “Half the world is composed of people who have something to say and can't, and the other half who have nothing to say and keep on saying it”. In other words, some discourses live long while some die very quickly. If ever one makes an effort, one would know the reason for its importance and understand that the answer for this lies in the art of using language effectively. Since man is a social animal, his need for social acceptance is phenomenal and so is his ability to communicate. In an era of communication, the art of being a good communicator helps gain an edge over the others who are unable to put their actions into the right words, thus, leading them to a communication failure. History has been a witness to all great orators who have moved nations towards a mission and driven people towards an aim merely on the basis of their powerful words. However, the question remains as to why few people create magic through their words, while others are barely able to make a coherent speech? The answer is language, communication and the art of rhetoric. Language is an essential element of human life. It is not only a means of communication but a powerful tool to express one’s personality. The word ‘communicate’ comes from the Latin word ‘Communicare’ which means ‘to impart, to participate, to share or to make common’i . When language is used to persuade somebody it is called rhetoric. Rhetoric means the art of using language whether in speech or in writing to bring about a change in the behaviour of people. Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary defines rhetoric as “the skill of using language in speech, or writing in a special way that influences or entertain people” and the world English dictionary defines it as “a speech or writing that is intended to influence people, but that is not completely honest or sincere”. Key Words: Communicator, oration, Rehearsals, Rhetori
İmparatorluk ve Cumhuriyet: Devamlılık ve Kopuşun Ötesine Yönelik ve Deneme, 2023
Bijdragen en Mededelingen betreffende de Geschiedenis der Nederlanden, 2001
Academia Biology, 2024
Roms unbekannte Grenze. Kelten, Daker, Sarmaten und Vandalen im Norden des Karpatenbeckens. 4. Jh. v. Chr. bis 4. Jh. n. Chr. (Schriften des kelten römer museums manching 8, 2018) 5-15, 2018
Apoteosis. De lo humano a lo divino. La figura del héroe, 2024
Yeditepe Yayınları , 2023
Ana Garduño Ortega, Ekaterina Álvarez Romero y Silvia Rodríguez Molina (eds.), El México antiguo. Colección del Museo Amparo, 2021
Nature, 2021
Jurnal Studi Ilmu-ilmu Al-Qur'an dan Hadis, 2021
The Herpetological …, 2009
The American Journal of Pathology, 2011
Hypertension Research, 2015
Correspondentieblad NMV, 2002
Estudios Públicos, 2014
Nuclear Physics B, 1997
Biophysical Journal, 2000
Archaeofauna, 2023
Chemosphere, 2007
Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2017
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The meaning of EXTEMPORANEOUS is composed, performed, or uttered on the spur of the moment : impromptu. How to use extemporaneous in a sentence. Did you know? ... If extemporaneous speaking is challenging, consider an improv class.
Mastering Extemporaneous Speaking: A Lifelong Journey. Now that you have the knowledge and tips to deliver an impressive extemporaneous speech, it's time to embark on your journey of mastering this valuable skill. Remember, extemporaneous speaking requires practice, patience, and a willingness to step out of your comfort zone.
• Extemporaneous speech: A well-prepared speech that relies on research, clear organization, and practiced delivery, but is neither read nor memorized. What is an Extemporaneous Speech? The word extemporaneous means "without planning" and is considered a synonym for the word impromptu. However, an extemporaneous speech is actually a well ...
Extemporaneous Speaking. Extemporaneous speaking is the presentation of a carefully planned and rehearsed speech, spoken in a conversational manner using brief notes. By using notes rather than a full manuscript, the extemporaneous speaker can establish and maintain eye contact with the audience and assess how well they are understanding the speech as it progresses.
Understanding Extemporaneous Speech. An extemporaneous speech is a type of speech delivered with little to no preparation, often with the help of notes or an outline. Unlike a memorized or read speech, an extemporaneous speech allows for more natural delivery and interaction with the audience, as the speaker can adapt to the audience's reactions and feedback in real-time.
Extemporaneous Speaking (Extemp, or EXT) is a speech delivery style/speaking style, and a term that identifies a specific forensic competition.The competition is a speech event based on research and original analysis, done with a limited-preparation; in the United States those competitions are held for high school and college students. In a Extemporaneous Speech competition, enrolled ...
Extemporaneous speech is a type of public speaking that combines elements of preparation and spontaneity, allowing the speaker to deliver a speech with limited notes while maintaining a conversational tone. This approach encourages speakers to be flexible and responsive to their audience, enhancing engagement and connection. It's often used in contexts like debates, interviews, or situations ...
Extemporaneous speaking is the art of giv-ing speeches on the spot - without notes or memorization - relying only on the speaker's depth of knowledge and their ability to ex-plain what they know in a coherent, engaging manner. As a category of forensics competi-tion, extemporaneous speaking (or "extemp"
An extemporaneous speech is an impromptu speech that is given without any prior preparation. This means that you won't have any notes or a prepared written speech to read from. Instead, you will be expected to deliver a speech on a given topic on the spot. ... This doesn't mean you have to yell, but rather speak with conviction and clarity. By ...
What is an Extemporaneous Speech? The word extemporaneous means "without planning" and is considered a synonym for the word impromptu. However, an extemporaneous speech is actually a well-prepared speech that relies on research, clear organization, and practiced delivery. It is neither read nor memorized, so it is never delivered exactly ...