Brought to you by:


Apple Inc.: Global Supply Chain Management
By: P. Fraser Johnson
This case focuses on the supply chain strategy of Apple Inc. (Apple). Set in early 2020, it provides a detailed description of the company's supply chain network and capabilities. Data in the case…
- Length: 20 page(s)
- Publication Date: Jun 1, 2020
- Discipline: Operations Management
- Product #: W20472-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Same page, Teaching Note
- Same page, Educator Copy
$4.95 per student
degree granting course
$8.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
This case focuses on the supply chain strategy of Apple Inc. (Apple). Set in early 2020, it provides a detailed description of the company's supply chain network and capabilities. Data in the case allows students to develop an understanding of Apple's source of competitiveness and to gain insights into the management of a large, complex global supply chain network that focused on the intersection of services, hardware and software. Students will obtain an understanding of the supply chain challenges faced by Apple, in the context of supporting its corporate strategy and growth objectives.
Learning Objectives
This case can be used in an undergraduate- and graduate-level courses on operations management, supply chain management, logistics, business strategy, or marketing. It provides an opportunity to appreciate the complexities of managing a complex global supply chain. After completing the case, students will be able to do the following: Assess Apple's supply chain, and identify its key competitive advantages. Quantify Apple's ability to generate value from its supply chain. Identify potential opportunities and challenges for Apple in improving its supply chain. Analyze the effects of the opportunities and challenges Apple faces in its growth and evolution.
Jun 1, 2020 (Revised: Nov 13, 2023)
Discipline:
Operations Management
Geographies:
United States
Industries:
Ivey Publishing
W20472-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Supply Chain Innovation
Designed by apple in california. made by people everywhere..
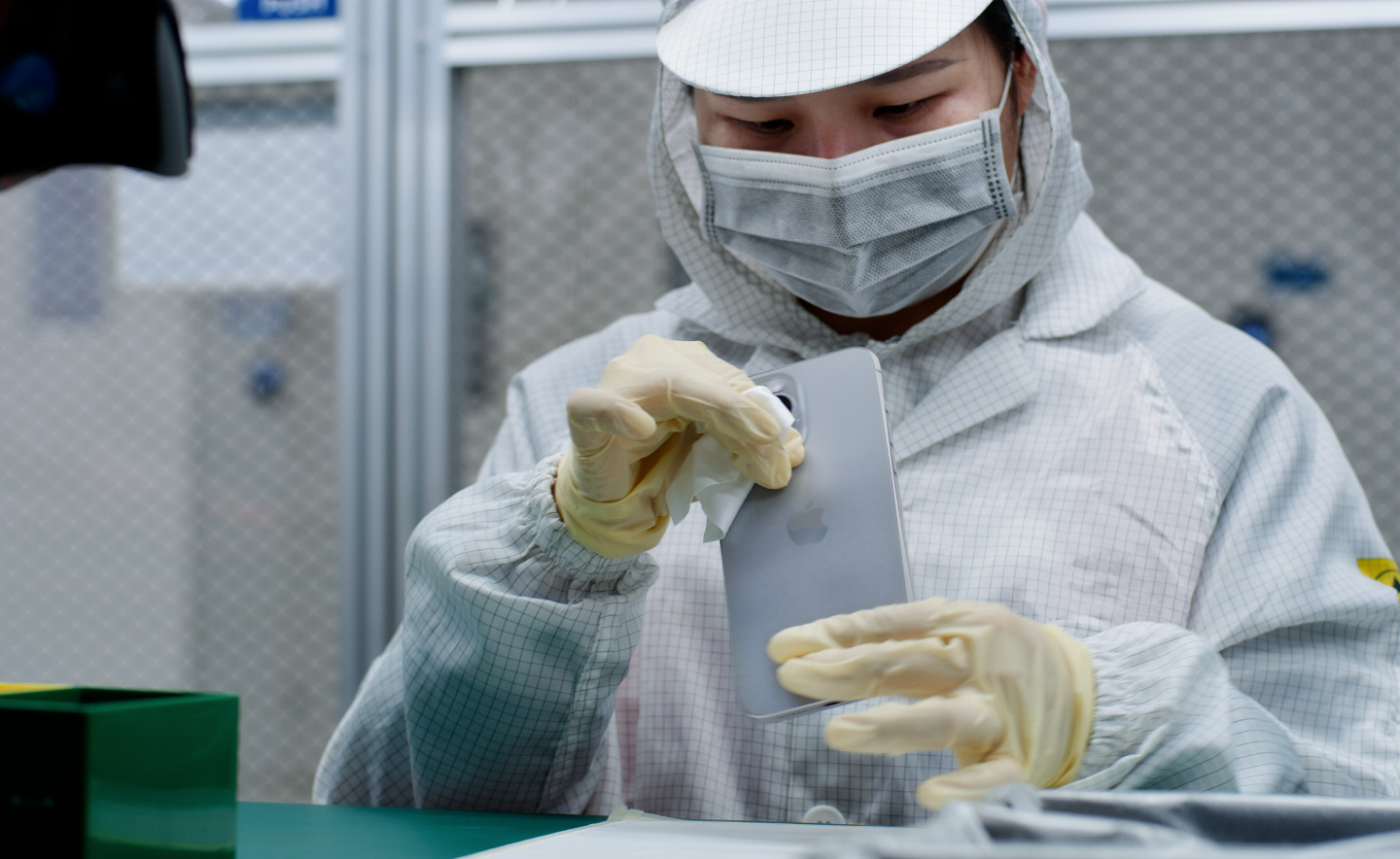

Business can and should be a force for good. We uphold our values everywhere we operate, supporting the people and communities across our supply chain, and working to protect the planet we all share.
A global supply chain.
Studio Display assembly, China mainland
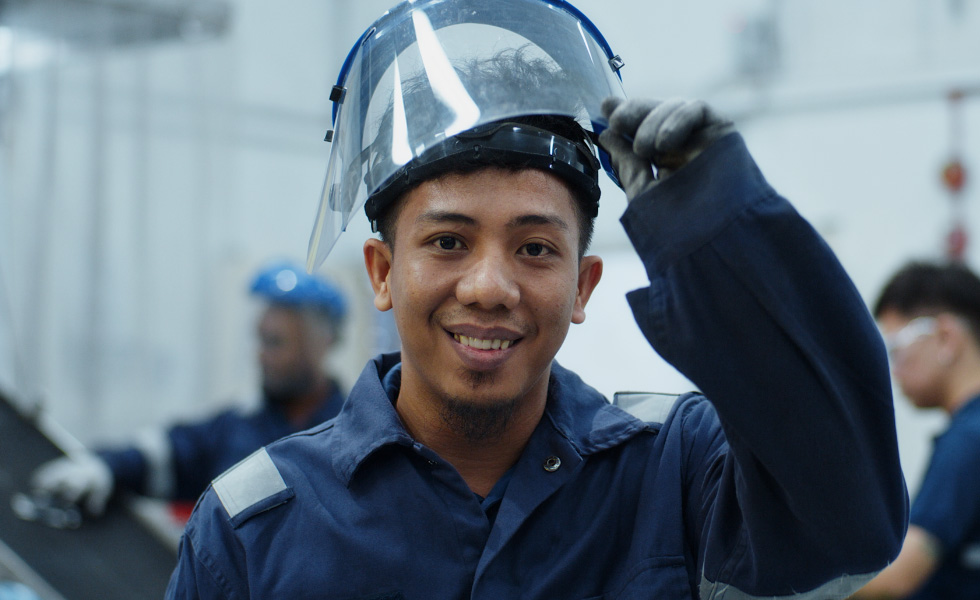

Apple products are made all over the world.
Thousands of businesses and millions of people in more than 50 countries and regions are part of our supply chain, contributing their skills, talents, and efforts to help build, deliver, repair, and recycle our products.
Our suppliers are required to meet the strict standards of the Apple Supplier Code of Conduct , no matter where they operate or what type of goods, services, or labor they provide to Apple.

Counterclockwise from top: Apple Watch assembly, Vietnam; Apple Watch band manufacturing, Japan; Mac Pro assembly, United States
We listen. And act.
Component manufacturing, Switzerland

We encourage everyone across our supply chain to share feedback. And we’re focused on ways to amplify their voices. We interview and survey hundreds of thousands of supplier employees, and provide hotlines so they can anonymously raise concerns directly to Apple. We use this feedback to support our suppliers in strengthening their operations and providing the best possible experience for their employees.
We investigate reported concerns quickly, with Apple experts typically arriving onsite within 24 to 48 hours. Apple has zero tolerance for retaliation, and any supplier found to have retaliated against an employee for raising a concern faces immediate consequences, up to and including termination of their business with Apple. We require our suppliers to promptly address any issues, and we regularly check on their progress until we confirm that all necessary actions have been taken.
If suppliers are unwilling or unable to correct any issues, they risk removal from our supply chain. Since 2009, we have removed 25 manufacturing supplier facilities and 231 smelters, refiners, and manufacturers of materials from our supply chain for failing to meet our standards.

Counterclockwise from top: Logistics, United States; Apple Watch assembly, Vietnam; iPhone assembly, China mainland
supplier employees directly engaged by Apple about their workplace experience in 2023
improvements made to supplier workplaces based on employee feedback in 2023, mostly focused on services like transportation and dining
people at 35 supplier sites reached by our hotline awareness campaign, which provides knowledge on how to raise workplace concerns
supplier employees contacted following interviews to ensure that they didn’t experience retaliation as a result of their participation
Labor and human rights at the foundation.
Apple Watch assembly, Vietnam
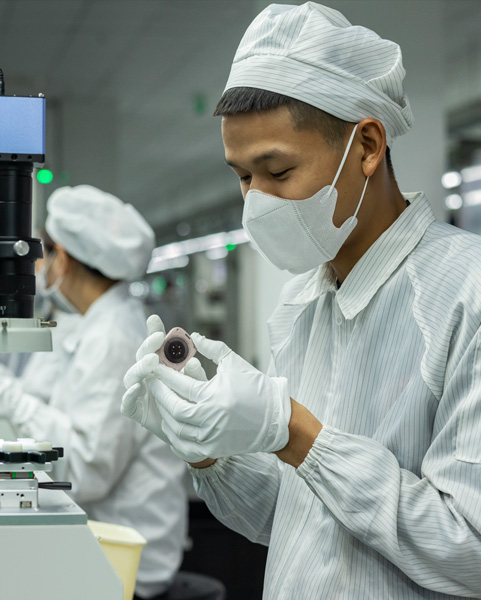

Everyone has the right to work in a safe and healthy environment where they’re treated with respect and dignity. We uphold these rights with every decision we make, including the suppliers we choose to work with, the materials we select for our products, and the processes and equipment we use to make them. We work closely with our suppliers to uphold the highest standards of labor and human rights everywhere our business reaches.
Our standards apply globally, regardless of where people live or work or which job they do. We require our suppliers to educate their employees on their workplace rights, including how to share feedback if their rights aren’t being respected. With the help of experts, nonprofit organizations, government agencies, and workers themselves, we consistently strengthen our requirements and programs to make sure they continue to meet the needs of people across our supply chain.

From top to bottom: Component manufacturing, India; Studio Display assembly, China mainland
supplier employees trained on their workplace rights since 2008
supplier employees’ working hours reviewed weekly to verify compliance with our standards
education and training sessions delivered through the Apple Supplier Employee Development Fund (SEDF)
Dedicated to continuous improvement.
Product personalization, United States
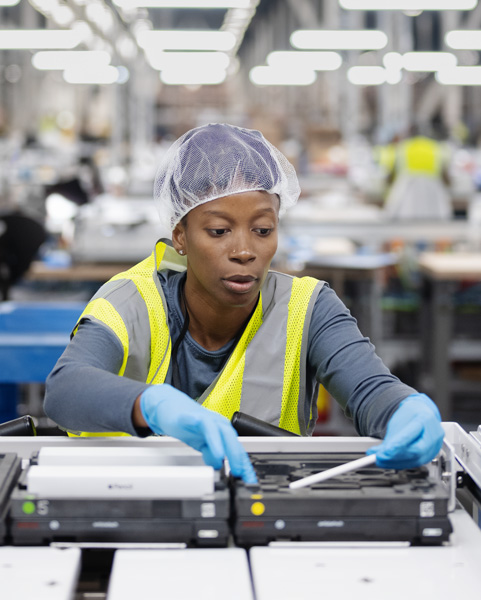

Before a prospective supplier enters our supply chain, we assess their ability to meet our standards and identify areas for improvement. We hold suppliers accountable for our strict standards through regular, rigorous onsite assessments. Conducted by independent third-party auditors, these assessments look at every detail of a supplier’s operations through worker and management interviews, detailed site walkthroughs, and thorough reviews of documentation.
Suppliers must fix any violation of our standards under the supervision of Apple experts and take steps to prevent the issues from happening again. Any suppliers that are unable or unwilling to improve their operations to meet our requirements risk removal from our supply chain.
We also support our suppliers’ continual learning and improvement by having Apple experts share knowledge, advise on best practices, and design learning plans customized to the needs of each site.

Clockwise from top left: HomePod assembly, Vietnam; Component manufacturing, Germany; Fiber-based packaging production, Austria
assessments of supplier facilities conducted in 2023, including 203 unannounced visits
of prospective suppliers prevented from entering our supply chain since 2020 for being unable or unwilling to meet our requirements
The strongest standards in hiring.
Mac Pro assembly, United States
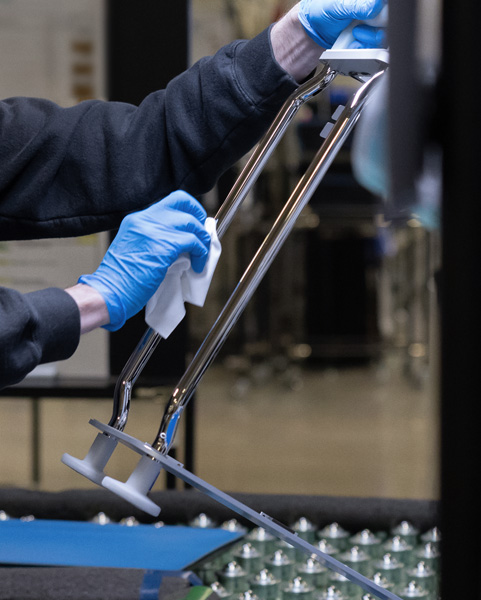

Apple has no tolerance for forced labor. Our policies that prevent forced labor apply globally, regardless of a person’s job, location, or how they were hired. We require that job recruitment processes be free and fair, prohibiting practices such as charging fees to secure a job — even where it’s allowed by law. We’ve partnered with the International Organization for Migration (IOM), a United Nations agency, to create easy-to-use tools that help suppliers recruit people ethically and with respect for their human rights.
Our work to prevent forced labor extends throughout the employment journey, and we verify that suppliers are meeting our standards every time we engage with them, including during assessments.
Learn more about our efforts to prevent forced labor (PDF)
instances found where people were forced to work in our supply chain in 2023
people trained on the industry-leading tools in the Apple Responsible Labor Recruitment Due Diligence Toolkit in 2023
in recruitment fees paid back by suppliers to more than 37,700 employees since 2008 due to Apple’s zero-fees policy
Skills that open doors.
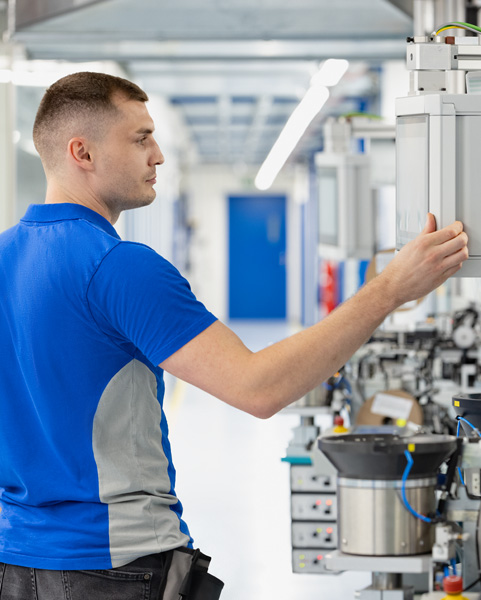

Through the Apple Education Hub, people across our supply chain are able to access technical education and resources on topics such as personal development, leadership, computer science, coding, robotics, recycling, and advanced manufacturing. These programs enrich supplier employees’ workplace experiences and provide the skills needed to pursue opportunities in highly technical fields. For example, graduates of our Swift coding program have launched apps on the App Store, meeting the high bar required for publication.
We partner with leading experts such as the Council for Adult and Experiential Learning (CAEL) in the United States, Zhejiang University in China mainland, and St. John’s Medical College in India to ensure that our programs are innovative, meaningful, and connected to relevant opportunities in local job markets.

Clockwise from top: Component manufacturing, Japan; Component manufacturing, India; Mac Pro assembly, United States
technical or management positions attained by graduates of our education programs
supplier employees who have graduated from our Swift coding program since 2017
The Supplier Employee Development Fund.
Apple Education Hub, China mainland
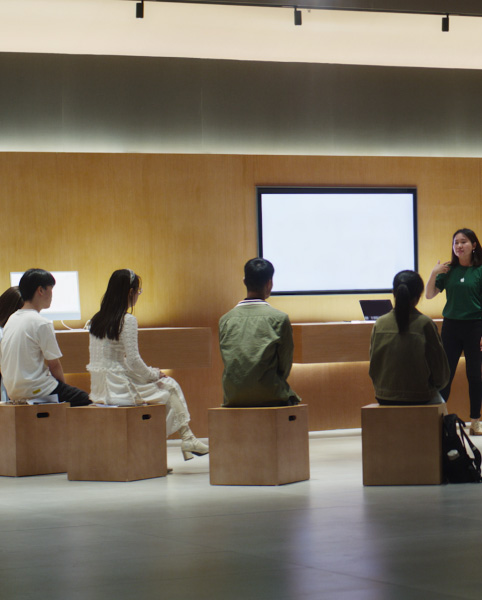

Education is a powerful equalizing force, and we are committed to providing opportunities for the people in our supply chain to learn and grow. In 2022, we announced a $50 million Supplier Employee Development Fund (SEDF) to further invest in people in our supply chain. Through the fund’s Apple Education Hub, we’re expanding access to educational opportunities for supplier employees and their surrounding communities.
In partnership with local academic institutions and non-governmental organizations (NGOs), the Apple Education Hub helps supplier employees develop the skills necessary to pursue new opportunities in our supply chain, as well as better manage their health and well-being.

From top to bottom: Component manufacturing, United States; Retail janitorial services, United States
supplier employee participants in learning and development opportunities through the Apple Education Hub in 2023
supplier employee participants in our education programs since 2008
Health starts with knowledge.
Education programs, India

Education programs, India
We’re committed to cultivating a supply chain where people can thrive — inside and outside work. This means providing the people in our supply chain with the tools needed to focus on their physical and mental health. Since 2017, millions of supplier employees have benefited from training on essential topics such as nutrition, reproductive health, early disease detection, and mental health. These programs are tailored to meet the needs of local supplier employee populations, equipping them with important knowledge and skills to take control of their own health, which they can then share with their communities to multiply the impact.

Counterclockwise from top: Health and wellness education, Vietnam; Health and wellness education, India; iPhone assembly, China mainland
people reached by our health and wellness programs since 2017
participants in our mental well-being programs in 2023
Advanced. Manufacturing.
Component manufacturing, United States

As we continue to drive innovation in our products, the machines used to build them must also advance. That’s why we’re always reviewing and strengthening our machine safety programs to help keep the people who operate manufacturing equipment safe on the job. We require suppliers to design safer equipment from the start and to conduct regular trainings on topics such as the use of safety devices, inspection basics, automation safety, and hazards associated with moving parts. We also require suppliers to regularly inspect equipment and safety procedures to confirm that machines remain in safe working condition and that the rules put in place to keep people safe are being enforced and followed. If we do find issues, we work with suppliers to correct them and prevent them from happening again.

Counterclockwise from top: Component manufacturing, Japan; Component manufacturing, China mainland; Component manufacturing, Germany
supplier sites enrolled in our new enhanced machine safety training in 2023
machines inspected for safety risks at 112 key supplier sites around the world in 2023
A culture of safety.
iMac assembly, Ireland

iMac assembly, Ireland
Everyone has the right to be safe at work, and we work hard to verify that the materials, machines, and processes used to make our products safeguard the health and safety of the people in our supply chain. We consistently update our industry-leading health and safety standards and confirm that our suppliers meet those standards through regular inspections. We also partner with our suppliers to build a workplace culture that puts health and safety at the forefront every day, including by offering training materials and providing ways for employees to speak up if they identify opportunities to improve safety practices.

Counterclockwise from top: Fiber-based packaging production, Austria; Mac Pro assembly, United States; Component manufacturing, Germany
supplier sites participated in safety training in 2023
Facility Readiness Assessments conducted before manufacturing began in 2023
Leading the way on smarter chemistry.
iPad assembly, Vietnam

Keeping workers and customers safe is a top priority that guides the decisions we make about the materials we use in our products. We require our suppliers to follow our industry-leading chemical safety standards to make sure that employees, communities, and the environment are protected against chemical hazards. This includes working together to use safer materials in our products and manufacturing processes, such as in the cleaners used during product assembly. By collaborating with leading experts and nonprofit organizations, we’re accelerating the adoption of safer chemicals across the electronics industry, fostering safer working conditions for people far beyond our own supply chain.

Counterclockwise from top: MacBook Pro assembly, China mainland; iPhone assembly, China mainland; Supplier water treatment facility, United States
suppliers reported data on the chemicals used in their facilities in 2023
new safer cleaners approved for use in our supply chain in 2023, with a total of 175 approved cleaners deployed to our suppliers since 2020
A carbon neutral supply chain by 2030.

Apple’s worldwide corporate operations have been carbon neutral since 2020, and we’ve set a goal to become carbon neutral across our entire supply chain, including the lifetime use of our products, by 2030.
Reaching our Apple 2030 goal means we first need to continue reducing the carbon emissions from our manufacturing processes. To make this happen, we’re designing our products to be less carbon-intensive, increasing our use of recycled and renewable materials, and transitioning our entire supply chain to 100 percent renewable energy. We’ll then use carbon removal to address the small amount of remaining emissions, starting with high-quality nature-based solutions, like those in Apple’s Restore Fund.
We’ve also called on our suppliers to decarbonize their Apple production by 2030, and we’re helping them get there through targeted programs and training that aim to improve their energy efficiency and identify sources of high-quality renewable energy.
Learn more about Apple 2030

Counterclockwise from top: Supplier solar array installation, Switzerland; Apple Watch band manufacturing, Japan; Apple Watch assembly, Vietnam
of Apple suppliers expected to be carbon neutral for their Apple production by 2030
gigawatts of renewable energy operational in the Apple supply chain
Environmental rights are human rights.
Responsibly managed forest, Austria

The global impacts of climate change are becoming more apparent by the day. Our approach to protecting the planet considers not only the environmental implications of every decision we make, but also the impact of those decisions on people, particularly those living and working in communities disproportionately affected by climate change. That’s why we consider our supply chain in the context of the local communities where our suppliers operate.
Low-income and historically marginalized communities too often bear the brunt of the effects of climate change. As part of our Racial Equity and Justice Initiative (REJI), we created the Impact Accelerator for Black-, Latinx-, and Indigenous-owned businesses focused on environmental solutions. The Impact Accelerator is just one way we’re helping ensure that those most affected by environmental challenges are also helping design solutions that dismantle the systemic barriers to addressing them.

From top to bottom: Supplier solar array installation, Germany; Supplier water treatment facility, United States
Black-, Latinx-, and Indigenous-owned businesses participated in the Impact Accelerator since 2020
A zero waste mindset.
iPhone assembly, China mainland

We’re dedicated to minimizing our resource use and waste as we build our products. We require our suppliers to avoid sending waste to landfills by implementing recycling and reuse programs and developing innovative materials and recycling strategies. Today, all established final assembly sites for major Apple products are Zero Waste Certified.
Water is a critical resource shared by people and ecosystems around the world, and we’re working to protect it for future generations. Through our Clean Water Program, we’re helping suppliers reduce their water usage, promote water recycling, and prevent water pollution. Since the launch of this program in 2015, 20 of our suppliers’ facilities have achieved certification through the Alliance for Water Stewardship (AWS), the world’s leading water stewardship organization. Earning this certification requires suppliers to adopt industry-leading water conservation and stewardship practices while also engaging with their community to protect resources across their local water basin.

From top to bottom: Apple Watch band manufacturing, Japan; HomePod assembly, Vietnam
metric tons of waste diverted from landfills by Apple suppliers in 2023
gallons of freshwater saved through Apple’s Clean Water Program since 2013
Our journey to 100% recycled and renewable.
Materials recovered by Daisy, Apple’s iPhone disassembly robot, United States

Our goal is to one day build our products using only recycled and renewable materials and eliminate our reliance on mining. Each year, we move closer to that goal, with more components being made with 100 percent recycled or renewable materials. Effectively disassembling and recycling our products after their use is also a key part of our work to support a circular economy. These processes help recover valuable materials that can be used again, making the best use of limited resources and enabling us to design and build the next generation of devices to be even better for people and the planet. That’s why we help our suppliers efficiently and safely recycle our products, by providing Recycler Guides and conducting assessments to verify that they’re meeting our standards.
We maintain strict standards for the responsible sourcing of materials — whether primary or recycled. Since Apple doesn’t directly purchase or procure primary materials, we work closely with our suppliers to uphold these standards and work with partners to improve conditions in and around mining communities.
Clockwise from top: Daisy, Apple’s iPhone disassembly robot, United States; Supplier hydroelectric energy facility, Austria; Recycling, Singapore
responsibly sourced key materials in batteries, whether primary or recycled
recycled cobalt targeted to be used in all Apple-designed batteries by 2025 *
recycled rare earth elements targeted to be used in all magnets across Apple products by 2025

Read our 2024 reports to learn more about our dedication to people and the planet.

More from Apple on our global supply chain.
Your feedback makes a difference..
We welcome your thoughts, questions, and ideas about our global supply chain.
Our values lead the way.
Environment.
We’re committed to bringing our net emissions to zero across our entire carbon footprint by 2030.
Inclusion and Diversity
We’re holding ourselves accountable for creating a culture where everyone belongs.
Racial Equity and Justice Initiative
We’re addressing systemic racism by expanding opportunities for communities of color globally.
We empower students and educators to learn, create, and define their own success.
We design every product and service to keep your data safe and secure.
Accessibility
Our built-in accessibility features are designed to work the way you do.

Apple’s supply chain dynamics: An in-depth exploration
Apple, the technology giant, has established itself as a leader in the global market, known for its innovative products and seamless user experience. Behind this success lies a complex and vast supply chain that spans continents and involves numerous suppliers. This article explores how the scale and complexity of Apple’s supply chain influence global markets, examining the company’s efforts towards sustainability, the challenges it faces , and the controversies that have surrounded its supply chain.
The scale and complexity of Apple’s supply chain
Apple’s supply chain is a massive network that involves thousands of suppliers and partners worldwide. From sourcing raw materials to manufacturing and distribution, every step in the process is meticulously coordinated to ensure a seamless supply of products. This scale and complexity enable Apple to meet the demands of its global customer base while maintaining high standards of quality and efficiency.
The supply chain starts with the sourcing of raw materials, including metals, plastics, and glass, from various regions around the world. These materials are then transported to manufacturing facilities, mainly located in China, where they are transformed into components and assembled into final products. The finished products are then distributed to Apple’s retail stores and authorized resellers worldwide.
To provide some context, the below image shows all of Apple’s first-tier supplier (and customer) relationships as generated by our Supply Chain Links Monitor tool.
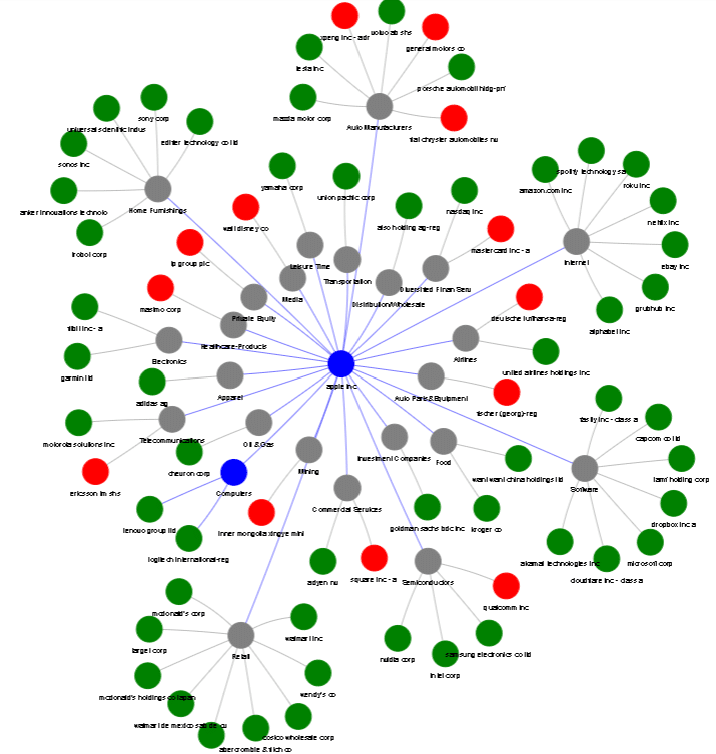
Providing a comprehensive overview, the visual representation below delves into the intricate labyrinth of Apple’s primary supplier (and customer relationships). This intricate web not only underscores the complexity of Apple’s supply chain but also offers a glimpse into the interwoven relationships that extend into the second and third tiers (available to see in our Business and Enterprise versions ). Beyond the immediate connections, the second and third tier relationships reveal the ripple effects and dependencies that characterise the dynamics of the supply chain ecosystem.
Supply chain sustainability efforts by Apple
Recognizing the environmental impact of its operations, Apple has made significant efforts towards supply chain sustainability. The company has set ambitious goals to reduce its carbon footprint, conserve water resources, and minimize waste throughout its supply chain. Apple also works closely with its suppliers to ensure they adhere to strict environmental standards and ethical practices.
To achieve these sustainability goals , Apple invests in renewable energy projects, such as solar and wind farms, to power its facilities and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. The company also collaborates with suppliers to implement energy-efficient manufacturing processes, recycling programs, and responsible waste management practices. These initiatives not only benefit the environment but also contribute to cost savings and operational efficiency.
Challenges faced by Apple’s supply chain
Operating a vast and complex supply chain comes with its fair share of challenges. Apple faces the constant pressure to meet high customer demand while maintaining quality standards. The company must manage risks associated with supply chain disruptions, such as natural disasters, political instability, and changes in regulations.
Additionally, as technology advances rapidly, Apple must continuously innovate and introduce new products to stay competitive. This requires close collaboration with suppliers to ensure the timely availability of components and materials. With the ever-changing landscape of the technology industry, Apple’s supply chain must remain agile and adaptable to meet evolving market demands.
Issues and controversies surrounding Apple’s supply chain
Despite its success, Apple’s supply chain has faced scrutiny and controversies over the years. One of the major concerns is the treatment of workers in its supplier factories, particularly in regions like China. Reports of long working hours, low wages, and poor working conditions have tarnished Apple’s reputation and raised questions about its commitment to ethical practices.
Another issue is the use of conflict minerals in Apple’s supply chain. These minerals, such as tin, tantalum, tungsten, and gold, are sourced from regions associated with human rights abuses and environmental degradation. Apple has taken steps to address this issue by implementing rigorous due diligence processes and working towards a conflict-free supply chain.
Addressing criticisms of Apple’s supply chain
Apple acknowledges the criticisms and has taken steps to address them. The company has implemented supplier responsibility programs, conducting regular audits to ensure compliance with its standards. Apple works closely with suppliers to improve working conditions, provide training opportunities, and promote fair wages. It has also increased transparency by publishing annual reports on supplier responsibility, detailing progress and challenges faced.
Furthermore, Apple has actively engaged with non-governmental organizations and industry groups to collaborate on improving supply chain practices. By collaborating with stakeholders, Apple aims to create a positive impact beyond its own operations and influence the industry as a whole.
Apple’s influence over its suppliers
Apple’s size and market dominance give it significant leverage over its suppliers. The company sets strict standards and expectations, requiring suppliers to meet stringent quality, environmental , and labour standards. This influence extends to product design, where Apple collaborates closely with suppliers to ensure seamless integration of components and materials.
By working closely with suppliers, Apple can maintain control over its supply chain and ensure the delivery of high-quality products to its customers. However, this influence also comes with the responsibility to ensure fair and ethical practices throughout the supply chain.
Impacts of Apple’s supply chain on global markets
Apple’s supply chain has a profound impact on global markets. The company’s ability to manufacture products at scale and deliver them efficiently has disrupted traditional models and reshaped industries. Apple’s success has inspired other companies to adopt similar supply chain strategies, emphasizing efficiency, quality, and innovation.
Moreover, the demand for Apple’s products has created a ripple effect throughout its supply chain, benefiting suppliers and local economies. The scale of Apple’s operations has created job opportunities and economic growth in regions where its suppliers are located. The company’s influence has also driven technological advancements and encouraged collaboration among suppliers to meet Apple’s standards.
Successful initiatives within Apple’s supply chain
Within its vast and complex supply chain , Apple has implemented several successful initiatives that have had a positive impact. For example, the company has made significant strides in reducing carbon emissions by transitioning to renewable energy sources and promoting energy-efficient manufacturing processes. These initiatives have not only reduced environmental impact but also yielded cost savings for Apple and its suppliers.
Apple has also focused on responsible sourcing of materials, working to eliminate the use of conflict minerals and promoting recycling programs. By partnering with suppliers, Apple has been able to create closed-loop supply chains, where materials from old devices are reused to manufacture new products. This circular approach reduces waste and conserves resources.
The future of Apple’s supply chain and its global market influence
As technology continues to evolve, Apple’s supply chain will face new challenges and opportunities. The company is likely to continue its efforts towards sustainability, pushing for further reductions in its environmental impact and promoting ethical practices throughout the supply chain.
Apple’s influence over its suppliers will remain significant, as the company strives to maintain its position as a market leader. However, with this influence comes the responsibility to ensure fair labor practices, worker welfare, and environmental stewardship.
In conclusion, Apple’s scale and complexity of its supply chain have shaped global markets, driving innovation, and setting new standards. Through its sustainability efforts and initiatives, Apple has demonstrated its commitment to responsible business practices. As consumers increasingly demand transparency and ethical sourcing, Apple’s supply chain will continue to be a critical factor in its success and influence on the global market.
Request data on Apple’s supply chain links
Ready to delve deeper into Apple’s intricate supply chain networks? Uncover nuanced data and gain unparalleled insights and supply chain transparency with our data. Elevate your understanding of Apple’s operations, risks and challenges. Request bespoke data tailored to your specific inquiries and navigate the complex web of one of the world’s technology giants by getting in touch below.

Register interest for our trading co-Pilot
Let us know below.
- Programs Overview
- MSc in Management
- Full-Time MBA
- Accelerated MBA
- Accelerated MBA for HBAs
- Executive MBA
- Master of Management in Analytics
- The Ivey Academy
- Pre-Ivey Experiences
- Ivey Asia - Executive Education
- Faculty & Research Overview
- Faculty Directory
- Area Groups
- Centres & Institutes
- Ivey Impact
- Purpose, Mission and Values
- Strategic Planning
- Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
- Careers at Ivey
- Ivey Idea Forum
- Media Centre
- Contact Communications
- Alumni Overview
- Get Involved
- Benefits & Services
Apple Inc.: Global Supply Chain Management
Nov 12, 2020
- Apple Podcasts
Fraser Johnson , professor of operations management at the Ivey Business School, joins host Matt Quin to take another look at his award-winning case, Apple Inc.: Managing a Global Supply Chain (2014), as well as the recently published update, Apple Inc.: Global Supply Chain Management (2020). In this episode, Johnson and Quin discuss Apple's business model, how he has brought the company into the classroom over the years, and why junior faculty ought to consider writing cases. Professor Johnson is the Leenders Supply Chain Management Association Chair at the Ivey Business School, Western University, where he teaches courses in supply chain management and operations. Johnson is also the Director of the Ivey Purchasing Managers Index , one of the most widely watched and utilized indicators of future economic activity in Canada.
Hi, I'm at Quinn. Thanks for joining us for decision point from Ivy Publishing at the Ivy Business School. Today we returned to another award winning and best selling case. Apple INC managing a global supply chain, originally published in two thousand and fourteen. Authoring Professor Frasier Johnson from the Ivy Business School, presents a snapshot of Apple up against competitors such as blackberry and Samsu. Unlike other companies with leading supply chains, such as Walmart, apple's approach to supply chain strategy and supplier management padded, investing far less in assets to support distribution. Instead, the company is now famous for its focus on innovation, new product development and brand management. In this episode we ask Professor Johnson about how apple was able to use its business model and supply chain strategy to help it continue capturing significant value from hardware sales. We also take a look at the updated two thousand and twenty case in the increased complexity for apple as it continues to add services in products to compete in the mature smartphone market. I hope you enjoyed today's episode. So, Frasier, thanks very much for joining us today. Apple was a really different company in two thousand and fourteen. What prompted you to write the case then, and how have you audit what's changed as you've taught it throughout the years? Well, apples a fascinating company. A lot of the cases that are done in the supply chain area tend to be with traditional manufacturing companies like Toyota or large retailers like Walmart, and one of the things that really interested me about apple was or business model with the IPHONE, with these annual product introductions, with big spikes in demand, and exactly how were they able to get their supply chain organized to be able to meet these big peaks in demand that they were facing. So the great thing about cases is it puts the student in the seat of a protagonist. This particular case Examines Apple from the perspective of Jessica Grant. She's an analyst with a Toronto based Money Management Firm. You, as an author, did a great job of giving students a primer of how apple was able to reach the margins with the iphones through supplier relationships and really tight coordination of the supply chain. Can you remind listeners what's at stake in the case for apple when it was set in two thousand and fourteen. Well, apple was one of the early innovators in the smartphone business and if you take a look at what's happened to the company over the last decade or so, the iphone is a way that apple connects with their consumers. Those they do things like sell services to individuals. Really, you know, the analogy that I use in the teaching note is that the iphone represents the the the razor that they used to be able to sell the blades to the consumers. So as apple looks to expand as market in the smartphone business, really what it does is give them a platform to be able to connect with their consumers. And from the students perspective, you're putting them in the role of the analyst in the case allows them to take a look at the entire business operation as opposed to taking the role of a functional executive with a specific functional related problem. So let's talk teaching notes for a second, because you've written a lot of case as many of them are best sellers. Let's dive into the teaching note part of this. In the teaching note you mentioned flexibility as a key part of the apple supplier management strategy. With recently apple moving away from mentell process. There's in away from Samsung as a screen supplier. It seems that the company is really continuing to embrace this approach of flexibility. What do you see in the company? Back in two thousand and seven when apple launched the iphone, they basically outsourced everything. HMM. So to bring a iphone to market they had to work closely with their suppliers. And the other interesting part of this is a short product life cycle of the IPHONE. They bring a new product ote every year and that was one of the it's one of the other important parts of the case. How do you work with suppliers where you're constantly launching and relaunching a new product every year, in selling product in the in the millions? So if you take a look at a company like Walmart, for example, they practice every day low pricing, so they try to minimize the bull whip effect and provide stable demand so they can work with their suppliers to reduce their total costs. Apples a complete opposite. They embrace variability. They have, as I said earlier, these annual releases with huge product introductions, with high volumes and then volumes taper off slowly until they bring out a new product and repeat the process all over again. And so you've built this in these comparators, in in the narratives. So one of the things that we know is important about the uptake of a case, in the sales of a case, is also the teaching note, and you write great teaching notes. You've mentioned apple versus Walmart. What are some other things that you try to include in a teaching note to help a faculty member use it in the classroom? What are your keys to success? Well, you know, what you want is, as somebody writing a case, to have a teaching note that resonates with other instructors. So when I say resonates, it's got to be something that they can relate to. It doesn't want to be so complicated that when they read the case and then take a look at the teaching note, become intimidated with the material that they see. They have to be able to understand it. They'd be had to be able to translate the material that you provided the teaching note into a classroom setting, so being able to talk about the issues at instructors face, including a teaching strategy appropriate questions to ask as part of delivery of the material are all very important. The other thing that I think is important to recognize is it before the case is completed, you've also got to write the teaching note. So don't publish the case and then come back to the teaching note a month later or two months later. Rate both documents simultaneously, because you have to use your teaching note as a quality control check to make sure that there's enough information in the case for the students and the instructors to be able to complete the analysis properly. And I know something you've done and our other colleagues have done is way to finalize that teaching note, if you will, until you've taught it a couple times and see how certain questions go or there might be some new information that comes out that you can include. So I know you've done that a few times as well. Right. Yeah, for many of the cases that I've written I will go back to the great staff at I've publishing and make revisions to the teaching note and perhaps to the case I'm talking about, minor at it to make in case issues have come up in the class discussion and I can help clarify the case by making qualifying statements. Sometimes when you're right a case, even with the editing process that you go through, sometimes students don't always interpret the information properly. So gives me a chance to be able to go back in and, you know, just a couple of sentences put not tend to clarify what certain peoples of data mean. For example, one of the tips that you gave is to try to not make things overly complicated. At the time of the case there's a lot happening at at apple with the five c being released. Profit margins were down slightly from, you know, two thousand and nine to two thousand and eleven. What do you think of and consider as you're writing a case to maintain that focus without, you know, there's a lot that you can put in a case. How do you remain so focused as an author? Well, I think that you're right a case in a particular point of time and as you as you say, you know, a lot has happened at apple in the last decade, or I guess thirteen years, since they brought out the first iphone, and you know the way that I view a lot of cases. You like my one an apple my other cases on Walmart and Amazon, is that they're almost live cases in the sense that, you know, I keep crack of what's going on in these organizations throughout the year before I teach the case so that we can use the information in the case is kind of a launching board, but we can also I can also incorporate through the introduction of power point slides, for example, and other information in terms of more recent developments. In the case of Apple, you see them, for example, insourcing more product buying the chip division from Intel and moving more to insourcing mode as opposed to an outsourcing mode, and that's the kind of stuff that you can incorporate into the class discussion. You've mentioned that you've released an updated case, which is great. We encourage faculty to do that and authors to do that. We welcome that and it's a smart thing to do because the cases evolve, the companies evolved in the situations, in the environment that the business is working evolved as well. Could you talk a little bit about the new case and the new complexities for Apple? Is As we sit here, in two thousand and twenty I wrote the first apple case, as you stated earlier, in two thousand and fourteen and if you take a look at what was happening to apple at that point, the sales for iphones were on the upsway and you know, if apple had a problem at that point, it was simply keeping up with demand. Now, if you take a look at what's happening in two thousand and twenty, the situation that the company faces and the challenges for its supply chain or are a lot different. As we talked about earlier, it's more moved to more of an insourcing model. On the other side of it, sales of the IPHONE are now starting to flatten out and the smartphone market is starting to mature. So we've see in back in two thousand and fourteen, apple competing in an environment where the markets growing margins are pretty healthy and it's having trouble keeping up with the man to in two thousand and twenty, where you're facing consecutive years of sales declines of the IPHONE and a maturing market with a lot of price pressure on margins. The other thing that you see with apple in two thousand and twenty compared to two thousand and fourteen is an increased emphasis on services. So one of the things that we can talk about in the new case is how does apple manage its services supply chain? So it really gives you a double edge. On one side we can talk about changes to the iphone and what apple does to manage its iphone successfully, but also how do they use the iphone in terms of its relationships and connectivity with its customers as part of its services supply chain? I've mentioned before how popular this case is. It's been climbing up the best seller list for years. Why do you think that is it? Is it the brand? Is it because the student can hold this thing in their hands and have a relation with with the company? What do you think is made us so popular? You know, I like to say cases like this teach themselves, and you know it's an overused line maybe in some areas, but students are familiar with the company, instructors are familiar with the company. The brand is strong. Even students that don't necessarily get excited about coming to class and talking in a case discussion do like the technology companies and I think there's something in the case for people that most people, particularly students, can relate to in terms of the technology and how they use their iphones and even the debate among the students in the class, among the iphone users versus the non iphone users. So every time I teach the case I ask you know, who's using apple products, and iphones included, and who's not using them, and why is that? You know, why do you like apple? Why do you use your products? On the other end of the spectrum, who are the Anti Apple people and why have they made a conscious decision not to participate in what I call in my new case apple ecosystem? And that kind of allows us to talk about the company strategy, which then evolves into a further more detailed discussion about how they're able to support Tho strategy with their supply chain capabilities. Yeah, it's a very accessible for for students of many Undergrad students, Grad students, high school students, can they can all take a different approach with it, but apple is a company is pretty accessible. Have there been any challenges or surprises when you've taught this where you go, oh, that's a different perspective or I have to remember to the include that in my next version of the case. Anything that comes to mind. The major event for me was in two thousand and nineteen as I was teaching the case and my supply chain management elective. And you know, as I'm standing up in front of the class talking about what's happening with a company in two thousand and nineteen, about exactly how much it changed at at Apple, and you know that point. You know after I, as I do after every class, I make notes to myself in terms of things that I want to remember for the following year, I made the decision that I commit the time to updating the case and writing and ended up doing that writing the case this year. So to me, you know, when you deal with cases like apple, you know a lot of the changes and things that happen, both in the classroom as a result of what happens at the company and as part of your preparation in terms of teaching the case. Is kind of evolutionary. Is of most revolutionary. Yeah, but eventually, you know, with companies like this, you do reach a point where you've got to think about revising the product, and that's one thing I want to give as a really good tip, and I don't want to overlook this, I'm just looking at some notes I've got here, is that the importance of immediately after the class, taking down notes as an instructor H who's either taught this case a number of times or just new to it. All the great case teachers that I've seen makeup point immediately, even at the breaks, of writing down some notes about ways it could be done differently or different things to approach or something that didn't go so well. So I want to make sure that if we hit that point for those that are listening, because that's such a great tip that I don't want to overlook. So anything else that you make a point of doing right before class or during a break or right after the class as a process for case teaching? Yeah, yeah, I think that this is maybe a minor point, but I think a relevant one. I think regardless of how many times you've taught a case and regardless of whether or not you're the one that wrote the case, and sometimes I think people that write cases can be too overconfident in terms of their level of understanding with the material to invest the time before class to get ready, regret, regardless of how many times you've taught the case. So don't just pick the file up and walk into class. US remind yourself about the essential details of the case and the case facts and think about how you're going to manage the conversation with the student. And, as I said earlier the debrief after class, every time I teach a case, I sit in my office after class and make note to my teach on the front of my teaching plan in terms of things that I would adjuster do differently or things that I want to remind myself worked well and to do. And that regular pays off, because I've seen you teach. You've welcome to a lot of our team members from I be publishing to watch a teach. So I've seen it at work. As we wrap up today on the discussion, I want to come back to the writing of cases. Do you have anything that stands out to you that you wish somebody had told you when you were just starting to write cases? Any any tips for new case writers as they ventured down this road? I think that you, as a new faculty member, writing cases is a is a great way to first of all learn about management practice and if you're writing feel cases working with companies in terms of material or case development, it gives you a chance to be able to talk to managers about some of the issues that they're facing and it keeps you current and, you know, being able to and you can do that through your research, certainly, but writing cases is another way to be able to stay in touch with what's going on in terms of management practice. The second point is a writing cases helps you establish credibility with your students. Students pay attention to the material that's being used in terms of the case studies, and if your name's on the author list of the case study that they're using, it tells the students that you know you're doing work in this area. These chances are they're probably not reading your research and helps establish some credibility in terms of your familiarity with the subject matter and the material that you're using in class. Well, that's fantastic. Thank you so much, Frasier, for taking the time to speak with us and, moreover, working with our team on publishing cases and bringing cases to the class. I know when we get a submission from you, our team always enjoys the process, so thank you for that as well. It's my pleasure. Thanks for the great job that everybody to I be publishing, does and supporting the word that the faculty does in terms of writing and publishing cases. If you enjoyed today's episode, subscribe to Decision Point on spotify or wherever you listen. Be sure to check out the show notes for links to cases, resources and more. have any feedback, send us an email at cases at IV DOC A.
- Ivey Publishing

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This case study will show you the analysis of Apple’s Supply Chain core processes, challenging issues and complexities of its operations. 1) Apple’s Supply Chain Model. Information about Apple Supply Chain is a bit here, there and everywhere, it’s kinda tough to find the actual case study.
After completing the case, students will be able to do the following: Assess Apple's supply chain, and identify its key competitive advantages. Quantify Apple's ability to generate value from its supply chain. Identify potential opportunities and challenges for Apple in improving its supply chain.
Apple’s worldwide corporate operations have been carbon neutral since 2020, and we’ve set a goal to become carbon neutral across our entire supply chain, including the lifetime use of our products, by 2030.
Define Apple’s supply chain competitive advantages and dependencies. Analyze the factors driving the need for transformation and their impact. Assess the options available in Apple’s global value chain adaptation to a deglobalizing world. Evaluate the strategy and tactics for Apple’s supply chain transformation.
This article explores how the scale and complexity of Apple’s supply chain influence global markets, examining the company’s efforts towards sustainability, the challenges it faces, and the controversies that have surrounded its supply chain.
Fraser Johnson, professor of operations management at the Ivey Business School, joins host Matt Quin to take another look at his award-winning case, Apple Inc.: Managing a Global Supply Chain (2014), as well as the recently published update, Apple Inc.: Global Supply Chain Management (2020).