

Advantages and Disadvantages of Digital Payment
Looking for advantages and disadvantages of Digital Payment?
We have collected some solid points that will help you understand the pros and cons of Digital Payment in detail.
But first, let’s understand the topic:
What is Digital Payment?
Digital payment is a payment method that uses electronic devices and online platforms to transfer money from one account to another. It is fast, convenient, and secure.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Digital Payment
The following are the advantages and disadvantages of Digital Payment:

Advantages of Digital Payment
- Convenience – Digital payments offer a high level of convenience, allowing users to make purchases from the comfort of their own home or on the go. This means that users don’t have to physically go to a store or carry cash with them, making shopping more efficient and streamlined.
- Security – Digital payments are often more secure than traditional payment methods like cash or check. This is because digital payments typically use encryption and other security measures to protect users’ financial information.
- Speed – Digital payments are fast and efficient, with transactions often processed in real-time. This means that users can receive and send money quickly, making it easier to complete transactions and move money around.
- Record-Keeping – Digital payments often come with record-keeping features, allowing users to easily keep track of their transactions and view their payment history. This can be helpful for budgeting, taxes, and other financial planning purposes.
- Global Reach – Digital payments allow users to make and receive payments from all around the world, regardless of physical location or currency. This means that businesses and individuals can easily connect with others in different parts of the world and conduct transactions seamlessly.
Disadvantages of Digital Payment
- Cybersecurity Risks – One of the biggest concerns with digital payment is the risk of cyber attacks. Hackers can try to steal personal information or money from digital payment systems, which can be a major problem for those who rely on them.
- Technical Glitches – Sometimes, digital payment systems can experience technical difficulties that can prevent users from accessing their accounts or making payments. This can be frustrating and stressful, especially if a payment needs to be made urgently.
- Dependence on Technology – Digital payment requires access to the internet and a device to make payments, which means that people who do not have access to these resources may be left behind. Additionally, if there is a power outage or technical issues with devices or internet, digital payments may not be possible.
- Fees – Some digital payment systems charge fees for transactions, which can add up over time. While some fees are small, they can become significant if a large number of transactions are made.
- Lack of Privacy – Digital payment systems often require personal information such as name, address, and bank account details. This information can be collected and used by companies for targeted advertising or sold to third-party companies for profit.
- Advantages and disadvantages of Departmental Store
- Advantages and disadvantages of AC Motors
- Advantages and disadvantages of BLDC Motors
You can view other “advantages and disadvantages of…” posts by clicking here .
If you have a related query, feel free to let us know in the comments below.
Also, kindly share the information with your friends who you think might be interested in reading it.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Definition, Advantages And Disadvantages Of Digital Payment System
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of finance, the advent of digital payments has been nothing short of revolutionary. In this article, we delve into the definition and myriad advantages that digital payments bring to the forefront of banking. In particular, we’ll examine the various types of digital payments, their merits, and the nuanced aspects that cater to the needs of corporate organizations, entrepreneurs, fintech, and business executives within the African economic terrain, with a keen focus on key businesses in Nigeria.
Digital Payment System
The digital payment revolution in Nigeria represents a transformative journey within the broader context of Africa’s economic landscape. Emerging as a response to the evolving needs of a dynamic society, the introduction of digital payments has unfolded as a pivotal chapter in the financial narrative of the nation.
In the not-so-distant past, traditional banking methods held sway, often entailing cumbersome processes and lengthy transaction times. However, with the advent of digital payments, Nigeria witnessed a paradigm shift that aligned with the country’s aspirations for a more efficient and technologically advanced financial sector.
This introduction of digital payments in Nigeria was not merely a technological upgrade; it was a catalyst for financial inclusion, empowerment, and economic growth. As the nation embraced digital platforms, a ripple effect permeated various sectors, reaching corporate organizations, entrepreneurs, fintechs, and business executives alike.
The trajectory of this introduction mirrors the broader trends in Africa, where nations are recognizing the potential of digital payments to bridge gaps, enhance financial accessibility, and stimulate economic activities. In Nigeria’s case, key businesses became pioneers, adopting digital payment solutions that set the stage for a more connected and agile financial ecosystem.
This sets the stage for a deeper exploration of the digital payment landscape in Nigeria, where innovative platforms and forward-thinking enterprises have played a crucial role in shaping the narrative of financial evolution. The journey from traditional methods to the digital frontier is not just a local phenomenon but a testament to Africa’s embrace of the future of finance.
How Does Digital Payment Systems Work?
Understanding the intricacies of the digital payment system requires a comprehensive exploration of its workings at both the local and global levels. In this detailed explanation, we’ll unravel the mechanics of digital payments, shedding light on the processes that govern transactions in Nigeria , Africa, and the broader international landscape.
Infrastructure and Connectivity:
Globally, the internet plays a pivotal role, serving as the backbone for online transactions. From mobile data networks to broadband connections, the level of connectivity determines the effectiveness of digital payment systems on a global scale.
Digital Wallets and Mobile Money:
Internationally, digital wallets like PayPal, Apple Pay, and Google Pay have become ubiquitous, offering a secure and convenient means of making online and in-store purchases. These wallets often leverage near-field communication (NFC) technology for contactless transactions.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Technology:
The global landscape has witnessed the rise of cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, underpinned by blockchain technology. This decentralized form of digital currency operates on a secure and transparent ledger, ensuring the integrity of transactions.
Security Protocols:
Integration with business ecosystem:.
The digital payment system operates as a dynamic force, shaping the financial landscape in Nigeria, Africa, and around the world. The synergy of technological infrastructure, diverse payment methods , and stringent security measures propels the evolution of digital payments.
As the world embraces a cashless future, the digital payment system stands as a testament to innovation, accessibility, and the interconnected nature of modern finance.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Digital Payment System
Advantages of digital payment systems.
The digital payment system has emerged as a transformative force, bringing a myriad of advantages that resonate across businesses globally. Let us unravel the multifaceted benefits associated with digital payments and delve into how these advantages positively impact businesses across diverse sectors and geographical boundaries.
Efficiency and Speed:
One of the primary advantages of the digital payment system is the unparalleled efficiency it introduces to financial transactions. Unlike traditional methods that involve manual processing and delays, digital payments enable swift and real-time transactions.
Cost-Effectiveness:
Digital payments contribute significantly to cost reduction for businesses. Traditional payment methods often incur hefty transaction fees, especially for cross-border transactions. In contrast, digital payments are generally more cost-effective, with lower transaction fees and reduced operational costs.
Enhanced Security:
Global accessibility:, financial inclusion:, data insights and analytics:, streamlined business operations:.
The advantages associated with the digital payment system create a transformative impact on businesses across the board. From efficiency and cost-effectiveness to enhanced security and global accessibility, businesses that embrace digital payments position themselves for success in the modern economy.
As the digital payment landscape continues to evolve, businesses stand to benefit from a more connected, efficient, and resilient financial ecosystem.
Disadvantages Of Digital Payment Systems
While the digital payment system has brought about transformative changes in the financial landscape, it is crucial to examine the potential disadvantages and their impact on businesses. In this segment of our exploration, we’ll delve into the challenges associated with digital payments and how they can negatively affect businesses across the board.
Security Concerns:
Technological infrastructure gaps:, digital divide:, transaction costs:, dependence on technology:, privacy concerns:, resistance to change:.
While acknowledging the disadvantages associated with digital payment systems, businesses can proactively address these challenges. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures, investing in education and digital literacy initiatives, and diversifying payment options to cater to various customer preferences can help mitigate the negative impact on businesses.
By navigating these challenges thoughtfully, businesses can harness the benefits of digital payments while safeguarding against potential drawbacks.
In conclusion, digital payments transcend being a mere technological convenience; they signify a profound paradigm shift in our approach to financial transactions. The surge of digital payments within the African economic landscape places a responsibility on corporate organizations, entrepreneurs, fintech, and business executives to seize this transformative momentum.
Consider this a resounding call to embrace the future of finance, capitalizing on the manifold advantages while adeptly navigating the accompanying challenges. The digital revolution has dawned, and those who swiftly adapt are poised to forge a trail to financial success. The experiences of businesses in Nigeria serve as a compelling illustration — their journey towards a cashless and connected economy is not just a practical evolution but a thrilling and rewarding endeavour.
Embracing this wave of digitization is not merely a choice; it is a strategic imperative for sustainable growth and resilience in an ever-evolving economic landscape. As we stand at the crossroads of tradition and innovation, the call to action echoes louder than ever. Let businesses be pioneers in this transformative era, riding the digital wave to unprecedented heights of efficiency, connectivity, and financial prosperity. The opportunities abound, and the time to embrace the future is now.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Digital Payment
- Digital Nepal
- Information and Communication
- Nepali Date Converter Tool

Digital Payment has proved to be the most popular option among a large number of people these days. It has almost shadowed the traditional form of cash payment while doing any kind of transaction. Why do you think people are shifting their interests to this form of online payment? Let’s find out in this article.
The major reason behind the popularity of digital payment is it requires very little time and works very conveniently. It has made online payment transactions possible with a single tap on the phone. You don’t even need to carry your wallet everywhere and you can shop, pay bills, eat at a restaurant using the mobile banking services on your phone. Besides that, digital payment has a lot to offer for us if we know how to use it well. Let us first discuss the advantages of digital payment.
Do Read: Connect IPS Review: Elevates the Standard of Digital Banking in Nepal
Digital Payment: Advantages
- Digital Payment can be done at any time, from any location around the globe.
- It makes huge money transactions easier and faster.
- It offers higher payment security.
- You don’t need to provide the details of your card or your bank account every time you do a mobile payment.
- It saves all kinds of processing costs that would occur if you had chosen to pay through your card or by cash.
- There’s no risk of your money getting stolen or lost when you pay online.
- You can easily keep a record of your payment details and all kinds of transactions that you make.
- Some mobile banking apps make your online payment experience better by offering different kinds of cash prizes and offers. You can enjoy it while paying your bills online.
How does digital payment work?
First of all, to understand digital payment you need to understand the mobile banking/payment apps that make digital transactions possible. These apps have been gaining a lot of popularity and admiration among their users. Some popular mobile banking apps of Nepal are as follows:
- Khalti Digita Wallet
- IME Pay- Mobile Digital Wallet
- Moru- Digital Wallet
- Global Smart
- Connect IPS
These mobile banking apps provide a more convenient and simple way of entry to your existing bank accounts. First and foremost, these apps ask for your card, bank account details. After connecting with the respective banks, they get access to your saved funds. You can now use the banking services from the app on your mobile phone to perform any kind of digital transaction. You can either send or receive money, check your bank credits and keep a record of your payments. This is how the digital payment system works.
Check out: Top 5 digital payment apps/wallets in Nepal
The mobile banking apps in turn receive a commission from the banks every time people make transactions with the help of it. These apps have been fostered ever since digital payment came into light. No doubt, they have made our works a lot easier.
However, do you think digital payment comes with only its good aspects? Definitely not. Everything has both its own pros and cons. While digital payment may be very helpful to us, there are some disadvantages to paying your bills online. Let us now shift our focus to the disadvantages of digital payment.
Read more: Namaste Pay; Digital Payment Service Launched by NTC
Digital Payment: Disadvantages
- While digital payment does make transactions easier, the apps that help you pay will certainly charge some costs. You will have to pay third-party payment service charges.
- Not all shops are equipped with the facility of online payment. So, it is not possible to perform digital payment in such cases.
- It might create privacy issues as you will have to share all of your transactions and account details with third-party services.
- There might sometimes be a case of your account being hacked and your money being misused.
All in all, if you take some safety measures and make transactions carefully, digital payment can make your day-to-day life a lot better and easier. It has made it possible to pay bills without using your wallet and make use of banking services without having to visit the bank. This surely is one of the many boons that the technology and internet have given us.
So, what do you think about digital payment services worldwide? Have you also been paying with the help of mobile banking apps? Let us know in the comments below.
NCHL to bring Alipay Plus in Nepal via ConnectIPS for QR pay
Bank services reach all over nepal after saipal expansion, steps to get a machhapuchchhre bank visa card with a photo, most popular, ime pay is offering 2500 cashback on nlic premium payment, cryptocurrency illegal in nepal: nepal rastra bank declares, top 5 digital wallets in nepal: updated (2024), esewa vs khalti: comparing two major payment service providers in nepal, latest posts, khalti becomes an official ticketing partner for npl 2024, jmev elight ev is launching soon in nepal with 420 km range, byd m6 ev launching soon in nepal, range up to 530 km, price, the debut npl 2024 season to be live on star sports.
© Copyright Techmandu 2022
- Digital News

Top 10 Advantages and Disadvantages of Online Payments
4th September 2024 12 Comments

Table of Contents
- 1 What Are Online Payments?
- 2.1 Tips to follow while making online payments
- 3.1 1. Speed of transactions
- 3.2 2. Convenience
- 3.3 3. Reaching global audience
- 3.4 4. Low transaction costs
- 3.5 5. Quick and easy setup
- 3.6 6. Variety of payment choices
- 3.7 7. Availability of more distribution channels
- 3.8 8. Easy management
- 3.9 9. Better customer experience
- 3.10 10. Recurring payment capabilities
- 4.1 1. Technical problems
- 4.2 2. Password threats
- 4.3 3. Cost of fraud
- 4.4 4. Security Concerns
- 4.5 5. Technological illiteracy
- 4.6 6. Limitations on amount and time
- 4.7 7.Service fees and other additional costs
- 4.8 8. Disputed transactions
- 4.9 9. Loss of smart cards
- 4.10 10. False identity
- 5.1 Latest posts:
The very purpose of setting up a business is to make profits. And the whole idea of making profits is possible only if your business offers its customers the ability to make payments. With technological advancements in recent years, online payments have become an inseparable part of the e-commerce industry. And, why wouldn’t they, considering the many benefits that come with online payment features.
While the concept of online payments isn’t entirely new, the COVID-19 pandemic has only accelerated the use of online payment methods like credit/debit cards, UPI, and mobile banking across the globe, but especially in India. As more and more businesses adopt online payment gateways in their portals, the importance of these e-payment services is increasingly becoming more of a necessity for both vendors and customers.
Enquire Now
Products Required: Payment Gateway POS Machine Reseller
What Are Online Payments?
Payments made over the internet are generally classified under ‘online payments’. These payments are done while purchasing products or availing any services, both online or offline. Online payments can either be one-off payments (like a purchase from Amazon) or recurring payments (like subscribing to Netflix). Some of the common methods of online payment include
- Bank transfers
- Digital wallets like PayPal or Google Pay
- Online credit/debit cards
- QR Codes / UPI
How Do Online Payments Work?
Here’s a very basic and also the most common model of how online payments usually work:
- A customer places an order on the merchant’s website
- The payment gateway gathers all the required data and information needed for the transaction to take place
- The data is then forwarded to the financial institution or the credit card company
- This is further transferred to the customer’s card company
- The bank then confirms the transaction and informs the merchant
- Finally, the merchant sends a confirmation message to the customer saying that they have received the payment
Check out:- The New Rbi Monetary Policy Guidelines 2022
Tips to follow while making online payments
Though online payments seem highly convenient and safe, there are a few things you need to be careful of, given the increased fraudulent happenings.
- Do not save card details: Most of us prefer to save our card details on our smartphones or other devices to avoid entering them every single time. But this is not advisable as it can be used for wrong purposes in cases of theft. Always make sure to erase your card details after every use.
- Never share your passwords: As cliche as it sounds, it is very important to follow this advice. Don’t share your passwords with anyone, and keep changing them regularly so that you don’t fall prey to hackers or any other cyber criminals. Have a strong password and enable the OTP feature to ensure maximum security.
- Avoid using public WiFi networks: No matter how much of a hurry you are in, you must always avoid making transactions via public computers or WiFi networks as there are high chances of data theft and other cyber attacks.
- Use private windows: Make sure you perform all your transactions on private windows and avoid all kinds of suspicious apps or websites that are not recommended by the app store. You can find out about such apps by looking for reviews and the number of downloads.
Advantages of Online Payments
1. speed of transactions.
For both the seller and the customer, online payments save a lot of time. People don’t have to wait in lines, take time to write checks, or wait for paper bills. They don’t have to wait for banks to clear their checks so that they can access the money.
For sellers, it saves a great deal of time since they don’t have to waste time printing and mailing bills. Online payments also decrease the chances of late payments. Since it takes less than a few minutes to complete a transaction, people will not forget it or put it off for later.
2. Convenience
People can pay for goods and services at any time of the day from any part of the world. It is easier to click a feature on your smartphone than to collect the correct amount of cash for your purchase. You don’t have to carry a lot of cash, get worried about theft or not having perfect change. With online payment options, you just need to remember a certain pin, and that’s it, your transaction is done! As simple as that.
DID YOU KNOW? In a survey conducted in 2020 to analyze the changing consumer sentiments concerning the COVID-19 pandemic in India, the respondents over the age of 40 were more inclined towards using credit and debit cards for payment. Contrary to this, UPI and online wallets were more popular with younger consumers.
3. Reaching global audience
One of the biggest advantages of having online payment gateways is that businesses can operate globally and have a customer base irrespective of geographical limitations. According to research , over 56% of online shoppers prefer to shop cross-border. So implementing online payment options on your e-commerce site will undoubtedly increase sales as you will be catering for a global audience.
4. Low transaction costs
In a traditional payment setup, businesses have to hire front-desk employees or cashiers to manage sales and payments. But with online payments, transactions take place in an automated environment. Merchants can set up online payment gateways with minimal investment and lower transaction costs.
5. Quick and easy setup
Instead of spending time on setting up a whole payment process that involves certain equipment and some extra employees, you can easily and quickly integrate online payment gateways for your business. However, before you choose the services of a particular vendor, you can evaluate the different options available in order to choose the best one.
6. Variety of payment choices
With online payment features, you can offer your customers a wide variety of payment options to choose from. People have their own preferences, and if they can find that option while purchasing from you, there are obviously more chances of them actually getting through with the transaction.
7. Availability of more distribution channels
As a business, having online payment options can benefit your distribution channels a lot. If you are ready to accept online payments, you can enter the affiliate domain and branch out your sales by displaying your products or services on other websites. It is a great way to increase sales.
8. Easy management
Online payments make it easier to manage and store your money and other financial data. For both vendors and customers, there are a lot of tools available on the internet that will help you with transactions. You don’t have to keep track of your finances and let the tools do the job. It only gets easier since you don’t have to carry cash or cards.
9. Better customer experience
If customers feel it is convenient to purchase from you while also being able to save money and time, then that automatically translates to a positive customer experience. And as a business, you must put customer experience above everything else. Implementing online payment options for your business is a great way to achieve it, as many people nowadays prefer online payments over cash or card transactions.
10. Recurring payment capabilities
Online payments have made subscription markets operate with ease. Earlier, people used to make cash/card payments at regular intervals. Now, payments are automated and people don’t have to actually remember to pay or take the effort to go all the way to the physical place of business to make their payments. This has made receiving and accepting payments easier for both the seller and the customer.
Disadvantages of Online Payments
1. technical problems.
Online payments are subject to technical failures or downtime, just like any other software that is dependent on technology. Though tech maintenance operations are announced in advance and usually take place during the night, sometimes, it can cause frustration among online shoppers. Especially when it takes place without prior warning, a lot of businesses experience heavy bounce rates.

2. Password threats
If you are a registered user with a website who uses online payments pretty often, there are high chances that the online portal can have access to your personal information or bank account details. Though most transactions use OTPs (one-time passwords), the need for password protection arises in such situations. Especially if you are someone who deals with different banks, you might face the risk of a privacy breach.
3. Cost of fraud
Just as more and more people are shifting to online payments and preferring them over other traditional forms of payment, so are cybercriminals. ID thefts, phishing attacks, and database exploits are becoming more common. In order to prevent these and increase security, businesses install a lot of payment-security softwares and eventually incur a lot of costs.
4. Security Concerns
As discussed in the previous point, using online payments come with a lot of security risks. Without proper security measures, fraudsters can easily hack important financial information and data. And since there aren’t any verification systems like facial recognition or biometrics, criminals can easily get away without getting caught.
5. Technological illiteracy
One of the main disadvantages of online payments is the technological illiteracy among many people, especially the older generation. Since they don’t have enough knowledge on how to go about using technology or smartphones, they refrain from using online payment methods. A lot of them also fear the complexities of it and continue to use traditional methods of payment. This is a huge drawback in developing countries like India.
6. Limitations on amount and time
Some banks limit the number of transactions you can do in a day or the maximum amount you can transfer in a day. Most online transactions also have a time limit under which you need to complete the process (like receiving and accepting OTPs). All these limitations can prove to be pretty inconvenient to some users.
7.Service fees and other additional costs
While implementing online payment gateways, some services may demand setup costs or even processing fees for customers using those facilities. Setting up online payment options obviously requires access to the internet and other services that come along with it. This easily leads to incurring extra costs and both the sellers and customers can find it tiresome.
8. Disputed transactions
If you find someone using your electronic money, you can file a complaint with your bank or online payment processor. However, if you are unable to find the personal details of the person or for that matter, any details about them, then you cannot file a complaint or receive a refund. It gets tricky in such situations.
9. Loss of smart cards
Most online payments are done with the help of credit/debit cards, ATM cards, or identity cards. So if you lose any of these, automatically, your online payment accounts that are linked to your cards will be at risk too. Of course, you can block your cards after informing the bank, but the time between losing your card and blocking it may prove to be risky as many transactions by fraudsters can take place during that time period.
10. False identity
Unlike physical transactions, there are no ways to identify if the person making the online payment is the one he/she is claiming to be. Since there are no verification methods like photographs or signatures, most online payments are done behind a veil of anonymity. This can lead to a considerable amount of forgery and identity theft.
Digital payments are shaping the e-commerce industry in ways more than one. As both a business owner and a customer, it is pretty much expected of you to have online payment options.
Though it is mainly considered to be advantageous for many obvious reasons, online payments have their own set of disadvantages that you need to be aware of. After all, in today’s digital world, every convenient feature comes with a bit of risk! With proper precautions and management, you can overcome most of these disadvantages.
NTT DATA Payment Services offers a complete payment solution to advance your business. With the help of our cutting-edge and seamless payment gateway services, you can step up your business in no time!
Latest posts:
12 comments.
- Pingback: 10 disadvantages of online bill pay - logindataworld
- Pingback: advantages of paying bills online - logindataworld
- Pingback: RBI Implements New Norms For Credit, Debit And Co-Branded Cards – All You Need To Know - NTT Data Payment Services India
- Pingback: What Is An Internet Merchant Account, And How To Accept Payments? - NTT Data Payment Services India
- Pingback: How Does a Payment Gateways Work? get to know in detail
- Pingback: advantages of online payment methods - logindataworld
- Pingback: advantages of online payment - logindataworld
- Pingback: advantages and disadvantages of online payment - logindataworld
I’m not sure where you are getting your information, but great topic. I needs to spend some time learning much more or understanding more. Thanks for excellent information I was looking for this information for my mission.
I like that you pointed out how online payments could save a lot of time, for both the seller and the customer. I was shopping around yesterday and I noticed that a lot of shops actually accept online payments now. It is nice to see that online payment is now common and could be used in a variety of ways, like online ticket purchasing.
It’s great that you elaborated on online payments and how they keep track of your online sales. My cousin is interested in starting a business in a few months, so he’d like to know more about an e-commerce payment system, and I think he’d benefit from your article. Thank you for the information on providing an accessible payment option for your customers.
This article does a great job of highlighting the key advantages and potential disadvantages of online payments. The convenience and speed of online transactions are huge benefits, but it’s also good to be aware of the additional security and fraud risks. Overall, a balanced and insightful perspective on the pros and cons of payment digitization.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

- Commercial Law
- Corporate Law
- Legal Studies Class XI
- Legal Studies Class XII
- Law Difference Between
- Consumer Protection Act, 2019
- Maternity Benefit Act, 1961
- Employees’ Compensation Act, 1923
- Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972
- Apprentices Act, 1961
- Payment of Bonus Act, 1965
Electronic Payment System: Types, Advantages, Disadvantages and Regulatory Bodies
An Electronic Payment System is defined as a mode of payment over an electronic network, such as the Internet. The Indian economy has developed at a rapid pace since the growth of e-commerce, electronic payments, and digital payments have gone a long way. Electronic payments have been rising since the implementation of demonetization and will continue to do so with the current government ensuring that these types of payments are promoted.
Geeky Takeaways:
- Electronic Payment System allows customers to pay for goods and services electronically without the use of cheques or cash.
- Businesses need a strong and secure electronic payment system in online dealings.
- Electronic Payment System is regulated in India by the RBI.
- The system is safe, speedy, and cost-effective in comparison with paper-based payment systems.

Table of Content
What is an Electronic Payment System?
Types of electronic payment system, advantages of electronic payment system, disadvantages of electronic payment system, regulatory bodies governing electronic payment system in india, regulations relating to electronic payment system, frequently asked questions (faqs).
Electronic Payment System allows people to make online payments for their purchases of goods and services without the physical transfer of cash and cheques, irrespective of time and location. The key components of this payment system are the payers and payees, financial institutions, electronic devices, communication networks, payment gateways, and mobile payment apps. As the global economy continues to evolve, the dependency on physical modes of payment is gradually giving way to digital alternatives that offer speed, convenience, and efficiency. These systems facilitate a diverse range of financial activities, from online purchases and bill payments to person-to-person transfers.
India, being the fastest-growing economy and a developing nation, has witnessed significant growth in various types of Electronic Payment Systems, driven by technological advancements and efforts to promote a cashless economy. The prominent types of Electronic Payment Systems in India range from the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) to Debit and Credit cards. Listed below are the types of Electronic Payment Systems:
1. Unified Payments Interface (UPI):
UPI has become a widely adopted and popular electronic payment system in India. It enables users to link multiple bank accounts to a single mobile application, allowing seamless and instant fund transfers between individuals and merchants.
2. Mobile Wallets:
Mobile Wallet services like Paytm, PhonePe, and Google Pay have gained widespread acceptance. Users can load money into these digital wallets and use the balance for various transactions, including mobile recharge, bill payments, and online shopping.
3. Debit and Credit Cards:
Debit and Credit card usage is prevalent in India, with various banks issuing these cards for electronic transactions. Cards are commonly used for Point-of-Sale (POS) transactions, online purchases, and cash withdrawals from ATMs.
4. Immediate Payment Service (IMPS):
IMPS enables instant interbank electronic fund transfers through mobile phones, internet banking, or ATMs. It is particularly useful for peer-to-peer transactions and small-value payments.
5. National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT):
NEFT is a nationwide electronic payment system that facilitates one-to-one funds transfer between bank accounts. It operates on a deferred settlement basis and is widely used for both individual and corporate transactions.
6. Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS):
RTGS is another electronic fund transfer system that allows real-time settlement of large-value transactions. It is typically used for high-value interbank transfers.
7. Prepaid Instruments:
Prepaid Instruments, including prepaid cards and gift cards, provide users with a convenient way to make electronic payments with a pre-loaded amount.
- 24/7 Accessibility: Electronic Payments can be made at any time, providing round-the-clock access to financial transactions.
- Global Accessibility: Users can make payments and transfer funds globally without being restricted by geographical boundaries.
- Instant Transactions : Electronic Payments are processed quickly, allowing for near-instantaneous transfer of funds between accounts.
- Faster Settlement: Compared to traditional payment methods, electronic transactions often result in faster settlement times.
- Record-Keeping and Tracking: Electronic Payment Systems facilitate easy record-keeping for both businesses and individuals.
- Encryption and Authentication: Electronic Payment Systems employ robust encryption and authentication protocols to secure transactions and protect sensitive information.
- Security Concerns: Electronic Payment Systems are susceptible to security breaches, including hacking, phishing, and identity theft.
- Technical Issues : Electronic Payment Systems rely on technology, and technical glitches or system failures can disrupt transactions.
- Fraud Risk: Despite security measures, Electronic Payment Systems are not immune to fraud. Unauthorized transactions, stolen credentials, or fraudulent activities can occur, leading to financial losses for individuals and businesses.
- Privacy Concerns : Users may be concerned about the collection and storage of personal information by electronic payment providers.
- Transaction Fees : Some electronic payment systems impose transaction fees, which can add up over time.
- The Regulatory Framework for the Electronic Payment System in India is governed by the Reserve Bank of India and other relevant authorities. The Reserve Bank of India has the authority to oversee and regulate payment and settlement systems.
- The Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 provides the legal framework for the regulation and supervision of payment systems in India.
- The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) issues guidelines for the UPI. The Information Technology Act, 2000 , provides a legal framework for electronic transactions and addresses issues related to electronic governance.
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI ) regulates securities and capital markets, and it also regulates electronic payments where security transactions are involved.
- The Ministry of Finance, through its various departments, provides overarching policy direction and guidance related to the financial sector, including Electronic Payment Systems.
- The Department of Telecommunication oversees the Telecommunications sector, and its regulations impact mobile-based electronic payment services. Mobile network operators and telecom service providers are subject to the regulations set by the DoT.
- The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) regulates the insurance sector in India. In the context of electronic payments, it may have oversight over the insurance-related transactions conducted through digital payment systems.
1. Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
The RBI plays a central role in regulating EPS in India through various guidelines and frameworks:
- Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007: This legislation provides the legal foundation for the regulation and oversight of payment systems in India. It empowers the RBI to supervise and regulate the functioning of EPS to maintain financial stability and consumer protection.
- Guidelines on Prepaid Payment Instruments (PPIs): The RBI issues guidelines that govern the issuance and operation of prepaid payment instruments, including digital wallets and prepaid cards. These guidelines outline parameters, such as issuance limits, reload limits, and Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements.
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI): The RBI regulates UPI, a real-time payment system, through guidelines that cover transaction limits, security protocols, and dispute resolution mechanisms. UPI has emerged as a popular channel for peer-to-peer and merchant transactions.
2. National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI)
- Operational Guidelines: NPCI develops and enforces operational guidelines for payment systems it manages, including UPI, Immediate Payment Service (IMPS), and Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS). These guidelines ensure standardized and secure operations.
- Security and Risk Mitigation Measures: NPCI implements security measures and risk mitigation strategies to safeguard electronic transactions. These measures include encryption standards, two-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring for potentially fraudulent activities.
3. Other Regulatory Bodies
Several other regulatory bodies also have a role in governing EPS
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) : SEBI, while primarily focused on securities market regulations, may have implications for EPS, especially in areas related to digital wallets and financial instruments.
- Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI): IRDAI oversees the insurance sector, and regulations related to EPS in insurance transactions may fall under its purview.
- Consumer Protection Regulations : Consumer protection regulations, focusing on transparency, disclosure, and dispute resolution, impact EPS to safeguard user interests.
- Data Protection and Privacy Laws : The introduction of data protection laws, such as the Personal Data Protection Bill, addresses concerns related to the handling and protection of user data within EPS. These regulations collectively form a robust framework, ensuring the secure and efficient functioning of electronic payment systems in India. It’s important to stay updated on any amendments or new regulations introduced by these regulatory bodies.
In conclusion, the Electronic Payment System refers to a mode of payment which does not include physical cash or cheques but rather includes Debit Card, UPI, etc. Regulated by the RBI, NPCI, and other regulatory authorities possess various legal issues but hold advantages too. The recent announcement of the linkage of fast digital payment systems of the central bank of India and Singapore, Unified Payments Interface (UPI) and Pay. Now, closely aligns with the G20 financial inclusion priorities of driving faster, cheaper and more transparent cross-border payments and shows that the future is in electronic payment systems.
1. What is UPI, and how does it work in the context of Electronic Payments in India?
UPI or Unified Payments Interface, is a real-time payment system facilitating interbank transactions. It allows users to link multiple bank accounts to a single mobile application, enabling seamless fund transfers and payments. UPI transactions are initiated through mobile apps, providing a user-friendly and efficient way to conduct digital transactions.
2. What measures are in place to ensure the security of Electronic Payment Systems in India?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) implements robust security measures for electronic payment systems. These include guidelines on encryption standards, two-factor authentication for transactions, and continuous monitoring to detect and prevent fraudulent activities. Additionally, financial institutions are mandated to comply with strict security protocols to safeguard user information and transactions.
3. How does the KYC process work for Mobile Wallets and Digital Payment platforms?
Know Your Customer (KYC) norms are enforced to verify the identity of users engaging in electronic transactions. For mobile wallets and digital payment platforms, users are required to provide specific identification documents to complete the KYC process. This ensures regulatory compliance and enhances the security of electronic payment services.
4. What role does NPCI play in the Electronic Payment Landscape of India?
The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) is a pivotal institution that operates and manages various retail payment systems in the country. NPCI oversees systems like UPI, IMPS, and NACH, contributing to the development and maintenance of efficient, secure, and interoperable electronic payment platforms.
5. How are Prepaid Payment Instruments regulated, and what types of transactions do they cover?
Prepaid Payment Instruments, such as mobile wallets and prepaid cards, are regulated by the RBI. The guidelines encompass aspects like issuance limits, reload limits and KYC requirements. These instruments facilitate a range of transactions, including mobile recharges, bill payments, and online purchases, providing users with a convenient and cashless payment experience.

Similar Reads
- Geeks Premier League
- Legal Studies
- Geeks Premier League 2023
- Mercantile Law
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
- Daily Current Affairs
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Monthly One Liner Current Affairs PDF
- Monthly Current Affairs PDF
- Last 6 Months Current Affairs PDF
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Reasoning Questions
- English Language
- Static GK Quiz
- General Awareness
- Banking Awareness Quiz
- Computer Knowledge Quiz
- BOOST Up PDFs
- Monthly PDFs
- Banking Awareness PDFs
- Expected Questions
- Stock GK PDFs
- Free Mock Test PDF
- Job Notifications
- Exam Analysis
- Exam Pattern
- Previous Year Cut Off
- Expected Cut Off
- Previous Year Question Papers
- Banking Awareness
- GA Questions Asked
- Study Plans
- Exam Review
- Interview Experience
- Descriptive Paper
- Privacy Policy

- Descriptive Contest
Essay – Digital Banking – Pros & Cons | Descriptive Paper Writing for Mains
Hello and welcome to exampundit . Here are the winners of EP’s Descriptive Contest Part 2. The topic “Digital Banking Essay – Pros & Cons” is topped by Pallavi and the runner-up is Pruthvi Ghanta.
Digital Banking Essay – Pros & Cons by Pallavi (Winner)
The drastic digitalization over the past few years has indeed affected almost every sphere of our lives. One of the most recent effects has been the move towards a cashless economy in India. Starting with the note ban in November 2016 due to the sudden withdrawal of the notes of Rs.500 and Rs.1000 denominations from the economy overnight, the Indian economy is going cashless.
In other words, least paper transactions will be involved, substituted by more digital transactions with the help of internet banking, digital wallets, Point-of-Sale machines, credit and debit cards, etc. These are having multiple implications on the economy with the following advantages and disadvantages.
ADVANTAGES:
- A cashless economy will allow less tension of tackling a wallet full of notes along with us, which is not at all safe in a world full of anti-socials. We can rather use our mobile as a one-stop solution for all kinds of transactions such as bill payments, fees payments, funds transfer, recharge, etc.
- It will ensure a ‘black-money free India’ or rather the so-called ‘parallel economy’ where people collect money in their closets at home without coming under the purview of tax .
- Crime rates have already started diminishing due to cash ban as most of the terrorist activities are funded with black money that has bore the brunt of this. In addition to this, other crimes such as burglary, extortion, bank robbery, etc. are also declining.
- One of the biggest advantages is the increase in the span of the income tax. Due to least involvement of cash, transactions have to be done through banks where proper KYC verifications will be done prior to banking transactions and hence, it will be easier for the Government to monitor and mend the income tax evasion by the unscrupulous persons. This will, in turn, enhance the revenue received by the Government.
Above all, the cashless economy will lead to the most convenient and secure economy for all.
DISADVANTAGES:
Apart from the brighter side of the digital economy , there are also some darker side associated with it as explained below :
- The cashless economy will see a hike in the hacking of the personal information over the internet such as credit and debit card numbers, PINs, passwords and other sensitive information due to an increase of digital transactions. In short, cyber crimes will escalate like anything if proper internet security measures are not taken.
- The poor section of India who is in majority and is scarcely covered under conventional banking system will suffer a lot, as they are solely dependent on cash for their daily wages.
- Sectors such as real estate, retail, restaurants, cement and other MSMEs, where huge cash transactions are involved are going to be affected terribly.
- Inadequate internet facility, low internet speeds, limited smartphone and broadband penetration, very less PoS machines are the roadblocks towards achieving full digitalization that is here the main substitute for cash transactions.
In short, a cashless economy can only be possible with sufficient infrastructure and planning that are required for supporting an economy like India.
Digital Economy – Pros & Cons by Pruthvi Ghanta
The term digital economy was first coined by Don Tapscott in his book “ The Digital Economy : Promise and Peril in the age of Networked Intelligence.
Few decades ago India faced severe problem , Nearly half of our country’s population didn’t have any form of identification, later Aadhar Cards provided digital identity to our people. Likewise now India is facing another problem of tax evasion and black money. So to curb these pitfalls Finance Minister Arun Jaitley in his Budget 2017-18 speech promoted digital economy with a string of measures to make e-transactions easier. Also Ratal.P.Watal who headed the committee on Digital Payments termed “ Digital payments are to finance what the wheel is to transport.”
Indian government is spending huge money for schemes to make people use digital currency like Digi Dhan Melas, schemes like Lucky Grahak Yojana, Digi Dhan Vyapar Yojana, No cash transaction above 3 lakh rupees, referral and cash back schemes to use BHIM app,etc., Government decided to remove all the duties on point of sale machines to promote digital transactions which is a part of govt’s target of 2500 crore transactions in 2017-18. Also banks have targeted to introduce additional 10 lakh PoS terminals by March 2017.
This is a good business opportunity for new companies like payments banks, Digital economy increases India’s tax base so that this amount can be utilised for more developmental activities. The cost benefit ratio is high using digital currency as there is no printing, manual security, life duration to the currency.
But in other aspects there are several problems using digital economy , the first and foremost one is security from hackers as many confidential passwords are stored online there is high probability that hackers may steal one’s personal information. In addition to this operational costs are high as the services offered charges as per your transactions like gateway fee, transaction fee etc. Another biggest problem vests with the illiterate as majority of Indians are living in rural and are illiterates, as they don’t know how to use these and they even don’t believe all this stuff.
So, by increasing banking penetration towards the masses, Decreasing the costs of Point of sale terminal, ensuring high security features to the digital economy may paves way to a New India.
Team ExamPundit
Latest Job Notifications
Sbi clerk 2023 notification out| sbi clerk recruitment 2023, ibps po notification 2023 – official announcement out, ibps rrb po and clerk notification 2023- official notification pdf, vacancy details out, rbi grade b recruitment 2023 notification out, ssc mts (multi tasking staff) notification 2023 out.
- Globalization
- Digital Payments: What they are, How they Work, and their Benefits and Problems
In recent months, all of us have heard extensively about the “war on cash”, the move to make India and other countries “ cashless economies ” and the general trend among policymakers worldwide to move the economies of the world to a digital and information enabled paradigm.
In this context, it is worth noting that the emphasis laid on digital payments and the digitization of commerce has implications for individuals, businesspersons, governments, and anyone and everyone who is a participant in the economy.
Thus, it is important to understand what digital payments and how they work and how they benefit the economy as well as the associated problems that accrue from using such modes of transactions and commercial dealings.
Digital Payments are payments that are conducted over the internet and mobile channels and hence, any payment that is sent online or through mobile computing and internet-enabled devices can be called such.
This means that for digital payments to take place:
We will come to the last part in a bit.
Apart from the sender having such means, the receiver of the payment too must have these ways to accept payments. This means that there must be a medium of transmission between the sender and the receiver wherein the former instead of paying the latter in cash and physical format pays in digital format meaning that the transaction happens over eCommerce or mCommerce modes of transmission.
Thus, what is important in any digital payment is the “via media” through which the payments happen which means that the intermediary and the modes of transmission are indeed the keys to making the transaction or the digital payment successful.
Coming to the intermediary, let us first think about what happens when we pay cash in the physical format. We first need to withdraw the cash from the bank or get it from someone who is likewise using cash obtained from the bank.
Thus, without banks and banking channels, there is no way we can access cash or transact for commercial dealings. Similarly, the digital payments need the intermediary as well and considering the fact that the payment still involves money though not in physical format and in digital format means that there must be infrastructure that connects the flow of digital cash across the payment value chain.
Remember that the payment value chain begins with the sender punching in the details in the Point of Sale devices at the merchant who in turn, uses the POS to connect to his or her bank account and thus, remits the money in such accounts. This means that the “digital backbone” is indeed important.
Now, while in developed countries, almost everyone has a bank account or has access to credit and debit cards in addition to most merchants having POS machines in their establishments means that the job of digital payments is infinitely easier than in developing countries where such infrastructure either does not exist or in basic form.
Thus, for countries such as India to move to the digital payment paradigm means that there is a massive need and demand to bring in all the players in the payment value chain into the digital backbone.
Further, when the Indian economy is predominantly cash-based one; this means that there is a massive effort to transition all the stakeholders in the payment value chain onto the digital paradigm. Considering that banking channels and access to banking services are mostly in urban areas, this means that there are huge challenges in migrating all the people into the digital network.
Moreover, as explained earlier, most merchants lack POS devices, and this is where service providers such as PayTM and the newly launched BHIM App from the government can do the trick.
In addition, as most of the country has already been covered under the Aadhar cards, it is easier for the government to create a digital backbone using such biometric models. Thus, while the road to a digital economy is indeed challenging, there exist the basic ingredients to smoothen the journey and all it needs is vision and dedicated effort from all stakeholders including the willingness of the people to make the journey.
Having said that, one must also caution that while a digital economy sounds like Utopia because black money, criminal activities, and corruption are supposed to (there is no tangible evidence from developed countries that they actually do) reduce, there are also pitfalls here since digital models are susceptible to hacking, identity theft, and cybercrime which raise pertinent questions about data integrity and data protection.
Moreover, in countries where the law enforcers are yet to come to terms with the digital paradigm, one must be realistic in expectations about the benefits.
Finally, digital payments are an evolutionary step towards the “ business at the speed of thought ” model that pioneers such as Bill Gates have always predicted would be the next step in our move from physical to digital and hence, despite the challenges and doubts, one must indeed take steps to move towards it.
Having said that, there is also a case to be made for proceeding gradually instead of the “shock therapy” and “big bang” method that has been pushed without adequate preparation.
Related Articles
- How Internet is Democratizing the World
- Loose Monetary Policies by Central Banks
View All Articles
Authorship/Referencing - About the Author(s)
The article is Written and Reviewed by Management Study Guide Content Team . MSG Content Team comprises experienced Faculty Member, Professionals and Subject Matter Experts. We are a ISO 2001:2015 Certified Education Provider . To Know more, click on About Us . The use of this material is free for learning and education purpose. Please reference authorship of content used, including link(s) to ManagementStudyGuide.com and the content page url.
- What is Globalization ?
- The Global Economic Crisis
- Introduction to the Global Economy
- Causes of Global Economic Crisis
- Impact of Global Economic Crisis
- Globalization - A Win-Win Situation
- Drivers of Globalization
- Globalization and its Discontents
- Globalization and Economic Crisis
- Lack of Regulation and the Crisis
- Paradigm Shift in Global Economy
- Derivatives & Global Financial Crisis
- Globalization and Young Workforce
- Globalization & Trickle Down Theory
- The Double Whammy of Austerity and Unemployment Confronting the West
- Historical Origins of the Present Global Economic Crisis
- Why We Should Not Let the Present Global Crisis Go Waste and Make Positive Changes
- BRICS: The Next Frontier for Investors
- Investing in Sin Industries: Are They Worth the Hassle ?
- The Future of Work
- Future of Work and Its Impact on Students and Professionals
- New Emerging Markets: Mexico, Indonesia, Nigeria and Turkey (MINTs)
- The Rise of Impact Investing and its Relevance to the 21st Century
- Ageing Populations in the West and their Impact on Healthcare Management
- A Comparison of Healthcare Systems around the World
- The Pitfalls of the Canadian Healthcare System
- The Benefits of Automation for the Healthcare Sector
- The Need for Accountability in the Healthcare Sector
- The Role of Electronic Healthcare Records in the Healthcare Sector
- Why is HealthCare Expensive in the United States ?
- Is India on the Brink of a Serious Economic Crisis?
- What is Health Insurance and the Different Health Insurance Systems around the World
- The Shock of Gray and Its Implications for the Healthcare Sector
- Why Europe is Broke and no amount of Central Bank Monetary Easing would Help
- How to Leverage the Demographic Dividend and Manage Demographic Deficit ?
- Why Growth is Stalling around the World ?
- Top Five Challenges Facing the Chinese Economy
- Top Six Economic Consequences of the Refugee Crisis
- The Ugly Face of Contract Farming
- What is Crop Insurance - Risks and Its Future
- Robot Advisors in Asia
- Why a United States Recession Seems Imminent ?
- India’s Demonetization Policy: Will it Work ?
- Demonetization and Its Impact on the Indian Economy
- The Promise and Peril of the Digital Economy
- Why Donald Trump Will be able to Stop Outsourcing ?
- The Economics of Drug Prohibition
- Is Australia Really Recession Proof ?
- South Korea: A Stunning Success Story
- Saudi Arabia’s Cash Crunch
- Socialism and Prosperity in the Nordic Countries
- Why Governments, Businesses, and Other Stakeholders must prepare for the Coming Age of Longevity
- How Firms and Corporates Grow in any Economy
- The H1B Visa Conundrum
- Can Jobs be Stolen ?
- Will Automation Kill the Economy ?
- Should Robots be Taxed ?
- The Internet of Things
- How Internet of Things (IoT) Will Impact Our Daily Lives?
- Is a Pollution Tax Worth it ?
- Is Dubai Really Tax Free ?
- The Chinese Internet Story
- Privatization of Water
- Economics of the Electric Car
- Rebuilding Americas Inner Cities
- Why Nations and Firms must Pursue Growth, but, Sustainably and Responsibly ?
- Different Growth Strategies for Firms Aiming to Become Market Leaders
- The Business Model of Amazon
- The Canadian Housing Bubble
- The German Small and Medium Enterprises (SME) Story
- Rags to Riches and Back: The Story of Chinese Boom and Bust
- The Singapore Growth Model
- How do Firms such as Uber, AirBnB, and Upwork Compete in the New Digital Economy ?
- Will London Still be the Financial Capital of the World ?
- Can the Government be Run Like a Business?
- The Argument for Privatization of Airports
- ERISA Act - The Government Mandated Stock Market Crash
- Global Race between American and Chinese Firms for Profitability and Survival
- Challenges Facing Indian Corporates Operating in a Low Growth Environment
- What the Current Wave of Protectionism and Populism mean for the Future of Globalization and Free Trade
- Turning the Heat On: A Case Study of the Indian Solar Industry
- The Kansas Experiment
- Game Changing Digital Governance Ideas: The Case Study of Aadhar in India
- How Genuine is China’s Growth Story?
- The Apple iPhone Controversy
- What Makes Some Cities and Regions Hotspots of Innovation
- Economic Impact of the Failed Coup in Turkey
- The Economic Impact of Cape Town’s Water Crisis
- Google: Conflicts of Interest
- The Benefits of Buying Local
- The Economic Effects of Digital Distractions
- The New Economics of the Music Industry
- Maldives: The Latest Victim of Chinese Debt Diplomacy
- The Why and How of Cities Worldwide Competing in a Race to Attract Investments
- Why Some Pharmaceutical Drugs are Very Expensive?
- The Ugly Side of Pharma Economics
- Fiat Currency and Trade Deficit
- Two Myths Surrounding American Economic Policy
- Amazon’s Vertical Integration
- Why are Wages Not Rising in America?
- The Rise of India as a Manufacturing Hub
- How Sports Became Big Business and Its Implications for All Stakeholders
- The Walmart-Flipkart Deal and Its Implications for the eCommerce and Retail Sectors
- Implications of Emerging Trends in Tourism for Developing Countries and Societies
- Case Study of the Indian Aviation Sector: Soaring High or Turbulence Ahead
- Early Bird Catches the Worm: Why First Mover Advantage Matters to Everyone
- How Singapore Became a World Class Regional Financial and Commercial Hub
- Historic Greek Debt Relief Deal and the Lessons for Other Nations from this Crisis
- Barriers to India achieving Double Digit Growth
- Effects of FIFA World Cup on the Economy
- Germany: An Economic Powerhouse
- Looking beyond BRICS for the Next Economic Hotspots
- Missed Call: A Case Study of the Indian Telecom Industry in the Post Liberalization Era
- What is FOMO (Fear of Missing out) and how it Impacts all of us in the Digital Age
- Smart Cities - What they are, How Realistic are they, and what can be done
- Has the internet lived up to its promise of an Egalitarian and Just World?
- The Power of Technology Firms over Our Lives
- Masters of the Universe: A Case Study of the Global Investment Banking Sector
- What is Ease of Business rankings and why do they matter to countries like India?
- What is Custo Brazil
- The Misconceptions about Poverty
- Switching Over From Socialism to Capitalism
- The AT&T - Time Warner Merger
- Strong Medicine: A Case Study of the Indian Healthcare Sector
- The Air India Fiasco
- The Argument against Planned Obsolescence
- Lionel Messi and Cristiano Ronaldo: Convicted Criminals?
- The Rise of E-Sports
- Braked Acceleration: A Case Study of the Indian Automobile Industry
- The Argentine Currency Crisis
- China’s Interest in Venezuela
- The Mouse Charmers: A Case Study of the Indian Information Technology Industry
- Kar Lo Duniya Mutti Mein: The Game Changing Case of Reliance Jio
- Finland’s Failed Universal Basic Income Experiment
- The Economic Implications of Facebook Data Breach
- Spotify: A Music Streaming App Worth $20 Billion!
- The Free Healthcare Debate
- The Gender Pay Gap Debate
- The Importance of Infrastructure Sector
- The Resource Curse: The Problem with Commodity Dependence
- The World of Private Equity
- Top 5 Economic Myths
- How A Private Money Market Would Work?
- Nation Branding
- The Problem with Antitrust Laws
- Why Electric Cars Aren’t Really Environment Friendly?
- National Competitiveness - Meaning and Its Myths
- The Problem with the United States Postal Service
- Why Facebook Wants To Be Regulated?
- The Impact of AMLO Win on the Mexican Economy
- Fighting a Price War
- The Problem with Modicare
- Wage Increases and Tax Cuts
- Should Infrastructure Spending Be Centralized?
- Should Prices Always Rise?
- Viking Economics
- Why India Should Abolish Personal Income Taxes?
- How Countries Can Reduce Tax Evasion
- Why India Must Revamp its Education Sector If it Wants to Become a Global Powerhouse
- The End of the Indian IT Sector
- Different Types of Online Business Models
- What Are Mobile Wallets?
- The Facebook Debacle and the “Own Your Data” Movement
- The Pros and Cons of Defense Spending
- The Impact of GDPR on Business
- Why Are Industrial Companies Acquiring Tech Startups?
- Apple’s Trillion Dollar Achievement and Also Some Forthcoming Challenges
- Can India Really Boycott Chinese Goods?
- Car as a Service (CaaS)
- Europe’s Controversial Common Agricultural Policy
- How Companies Are Avoiding Tariffs
- How the Sharing Economy Is Different
- The Ranbaxy Fiasco
- The Turkish Collapse and Its Effect on Europe
- America’s Response to China’s Belt and Road Initiative
- Data Localization: An In-Depth Analysis
- Factors behind the Rise of the Swiss Economy
- Symptoms of an Overheating Economy
- The Effect of Rising Oil Prices on the Indian Economy
- The New NAFTA Deal
- Universal Broadband: A Basic Human Right?
- Zimbabwe’s Road to Economic Recovery
- The Bangladesh Growth Story
- What Is China’s Deleveraging Strategy?
- Cannabis Legalization: Impact on Canadian Economy
- Cloud Kitchen: The Newest Innovation in the Restaurant Business
- Universal Basic Income in India: Examining the Arguments For and Against the Proposal
- Why Radical Disruption Is Not Always Beneficial: Lessons from Demonetization
- Do Farm Loan Waivers and Bank Bailouts Make for Sound Economic and Fiscal Policies?
- Power Shift: How the Internet Has Spawned a New Class of Powerbrokers in All Fields
- How Algorithms Rule Our Lives and What Businesses, Consumers, and Citizens Can Do
- Is the World Economy Dependent on America?
- The Ubiquitous Smartphone and How It Has Transformed Business and Commerce
- Impact of Crime on South African Economy
- Seattle’s Homelessness Crisis
- The Economics of Code Sharing Agreements
- Why Income Taxes Should Be Abolished?
- Can India Really Guarantee a Minimum Income?
- China vs. Taiwan: An Economic Comparison
- Why Wealth Tax has been Abolished All Over the World?
- How the Philippines Beat India at its Own Game
- The Economic Effect of the American Deep Freeze
- Who are HNIs and why they Matter in Both Positive and Negative Ways
- Pros and Cons of Opportunity Zones in America
- Should There be Reservations in the Private Sector and the Alternatives for Social Justice
- The Economics of Electronic Healthcare Records
- How North Korea Survives Sanctions?
- Why Jet Airway's Problems are Symptomatic of the Troubles in the Indian Aviation Sector
- Banning of Unregulated Deposits in India
- How 5G Will Affect Businesses?
- How Elections Impact The Economy?
- How The Chinese Slowdown Hit Apple?
- Pharmacy Benefit Managers: The Root Cause of High Healthcare Prices
- The Economics of Nuclear Weapons
- China’s Crackdown on the Gaming Industry
- Crackdown on Indian Credit Rating Firms
- The Financial Effects of An Indo-Pak War
- How Effective Are Sanctions In Enforcing Compliance and When Do They Backfire?
- Why Are American Companies No Longer Manufacturing Cars?
- Economic Impact of the Boeing Fiasco
- Executive Pay: The Curious Case of Carlos Ghosn’s Arrest
- Why Are Oil Prices Changing Gears?
- Government Spending vs. Government Taxation
- America’s Municipal Debt Problem
- Nigeria: A Strange Mix of Poverty and Oil Wealth
- The Apple “Credit Card”
- Is the American Dream Over? a Critical Commentary on the Future of the United States
- The Effect of the Trade Deal on American Farmers
- The Green New Deal
- Is the Indian Economy at Risk of Turning into another Greece or Thailand?
- The Two Conflicting Theories of Recession
- Why Is India Following a Loose Monetary Policy?
- Why is Sweden Facing a Currency Crisis?
- Drug Counterfeiting in India
- Economic Impact of Sri Lankan Attacks
- How China Destroyed Its Electric Vehicle Market
- Italy’s Citizen Income Proposal
- Focusing on Forecasting
- The Case against Free College Tuition
- The Instex Payment System
- As the World Ages, are we prepared to deal with the Consequences of the Shock of Grey
- What Explains the Decline of the Left in India and its Resurgence in the United States?
- Can Credit Card Interest Rates be Capped?
- How the Promised Utopia of Technology is Turning into a Perilous Dystopian Nightmare
- Why Indians Must Change Their Work Habits to Become World Class Professionals
- The Interconnectedness between the American Economy and the World Economy
- Canada’s Protectionist Economic Policies
- How will the Sino American Trade War End?
- The Diesel Downturn
- The Fight over Rare Earth Minerals
- The Sino American Trade War: Forced Technology Transfers
- Are Multinational Companies a Boon or a Bane?
- China’s Wealth Gap Problem
- Digital Cash: Advantages and Disadvantages
- Facebook’s Entry into the World’s Payment Systems
- Is Israel Really an Economic Miracle?
- The Trade Deal between America and Mexico
- The Economics of E-Waste
- Is the Indian Economy About to Return to the Decades of the Hindu Rate of Growth?
- Trust is the Key to Building Successful Companies and Great Nations
- The Debate over the Continuity of Policies When Governments Change and Implications
- Why there are Fewer Women in the Workforce and what can be done to rectify this
- Why Facebook must be Prevented from being used to Interfere in Elections Worldwide
- What Davos teaches us about Networking and Deal-making at the Highest Levels?
- How the Coronavirus Threatens the Global Economy and Lessons to be learnt
- Why the Present Job Crisis in India is a Perfect Storm of Converging Trends
- Are Indian Start-ups and eCommerce Firms Living in Fantasy Land without Profits?
- How the Coronavirus Outbreak Would Change the Way We Work and Live in the Future
- As the World Grind to a Halt, a Look Ahead at What is in Store for the Global Economy
- The Coronavirus Recession
- Coronavirus and the Fiscal Policy
- How Much Should the Government Help Struggling Businesses in Times of Crises
- How the Covid 19 Outbreak Has Exposed the Fault Lines in the Western World
- Why Businesses Must Prepare for Chaos and Confusion as the New Normal to Come
- Offshoring and Outsourcing Firms in the New Normal and what is in Store for Them?
- Why India Inc. Must Prepare for a Perfect Storm of Converging Crises
- Can Companies Really Exit China?
- COVID 19 and Its Impact on the Technology Sector
- The Power of Gatekeepers Who Control Data and Information in a Digital World
- The Impact of COVID-19 on Start-ups
- Impact of COVID-19 on Small Businesses
- Why Corporates Need to be Social Media Savvy in a 24/7 World Driven by Technology
- Why the Chief Technology Officer has become so critical to the Success of Corporates?
- How the Pandemic is a Nightmare for Small Businesses and Ways to Help Them
- Are Women Leaders Better Than Their Male Counterparts? Lessons from the Pandemic
- What is Commercial Arbitration and How Firms Use it to Settle Business Disputes
- Where Does the United States Go From Here and the Impact on Business and Economy?
- Does India Inc. Have a Diversity Problem? Should Indian Firms Do More for Inclusivity?
- Should Corporates Implement Affirmative Action as a Means of Ensuring Social Justice?
- The Glocal Approach in Business Is Applying Practical Intelligence in the Real World
- What is China Plus Strategy and Why it Can Become a Game Changer for the Indian Economy?
- What’s Behind the Big Tech Meltdown? Is It a Temporary Blip or a Longer Term Reckoning?
Electronic Payment Systems: Advantages and Disadvantages Case Study
Case overview and problem statement, methodology and analysis of the data, discussion of the results, summary and conclusions.
Depository institutions in the United States, the European countries, and in developing countries use the electronic payment systems. Clients of depository institutions have opportunities to use electronic payment systems for electronic fund transfers with the help of CHIPS, SWIFT, and Eurogiro systems; to use different types of cards; to perform online transactions; to withdraw the e-currency from electronic wallets and accounts; to pay bills; and to use the ATM. In spite of the popularity of electronic payment systems among customers and bankers, it is important to analyze them in terms of proposed benefits and possible weaknesses. Benefits or positive outcomes include the cost-efficiency, time-efficiency, the increased customer satisfaction, the increased industry competitiveness, the diversity of services, and possibilities for using e-currency and online banking. Weaknesses are associated with the work of non-reputable systems and issues of privacy and security.
There is a tendency of increasing the scope of using electronic payment systems in the national and international depository institutions markets because listed benefits. Paper-based systems are discussed today as expensive, slow, inflexible, and requiring many resources. On the contrary, electronic payment systems can provide clients with many services and improve the functioning of depository institutions. Therefore, it is possible to state that the used electronic payment systems have the significant impact on the depository institutions markets, and their progress depends on the systems’ effectiveness and further enhancements.
Electronic payment systems are actively used for money transferring and other transactions because they allow completing financial operations without the actual involvement of the paper documents exchange in the process. Modern electronic payment systems are presented in numerous forms, and it is possible to discuss debit, credit, and smart cards; electronic fund transfers; e-currency; and online banking as the most typical forms of these systems (Chin and Ahmad 4; Stinneford, Brown, and Davis 632). Depository institutions in the Unites States and globally are primary users of electronic payment systems of the listed types because they provide banks with opportunities to conduct instantaneous operations and transactions among accounts and other banks. As a result, more new electronic payment systems appear, proposing the wider opportunities to the clients of depository institutions (Aduda and Kingoo 109). The case is that the modern national and international depository institutions markets become more dependent on electronic payments, and this tendency is typical not only for the United States and developed European countries but also for a range of developing countries, where the banking systems begin to apply actively electronic payment approaches.
From this point, it is almost impossible to discuss the development of the depository institutions markets without analyzing the impact of electronic payment systems on them. Researchers and practitioners determine many advantages of such systems for implementing innovative strategies in banks. However, they also refer to limitations associated with the high security risks. The problem is in the fact that the exploitation of electronic payment systems tends to increase because banks refer to them as cost-effective and time-efficient methods for financial operations, and it is necessary to evaluate the actual impact of these systems on the scope of depository institutions markets. The purpose of this paper is to examine the existing literature on the problem, analyze the electronic payment systems’ benefits and limitations, and evaluate the overall impact of the systems’ integration on the development of depository institutions markets.
The review of the existing literature on the discussed problem is one of the typical approaches that can be used within the qualitative research methodology. In this context, the critical literature review method is effective to analyze the previous researchers’ findings in the area and determine tendencies in discussing the issue (Chin and Ahmad 4). This method of the critical literature review is selected for the current project as the most appropriate one because it provides the opportunity to overview many secondary sources and to compare the researchers’ findings regarding the electronic payment systems’ effects on the depository institutions as well as on the systems’ advantages and disadvantages. Journal articles for reviewing were searched for in such online libraries and databases as ProQuest, EBSCOHost, Science Direct, and Elsevier. The keywords used for the search were the following ones: ‘electronic payment systems’, ‘e-payment systems’, ‘electronic banking’, ‘electronic financial services’, and their synonyms. The articles were reviewed with the focus on searching and identifying factors that are important for evaluating the impact of the electronic payment systems on banks. In addition, the articles discussing the use of systems in the United States, the European countries, and the developing countries were selected.
The review of the literature demonstrates that there are factors having the positive impact on the scope of depository institutions, such as cost-efficiency; time-efficiency; the increased competitiveness; diversity of services; online banking; and e-currency. However, there are also factors that are characterized by rather negative effects on the banking systems’ development, and they include the privacy and security issues. The detailed analysis of these factors is important for conducting the overall evaluation of the systems’ impact on the depository institutions market in the United States and globally.
Cost-Efficiency
Electronic payment systems operated in banks are based on online transactions that can be discussed as rather cost-efficient for depository institutions. Hasan, Schmiedel, and Song state that banks spend less money for online transactions in contrast to paper transactions (Hasan, Schmiedel, and Song 165). In their turn, Aduda and Kingoo also accentuate the cost-efficiency of online operations noting that banks need to handle and transport the large amounts of paper documents daily in order to address the needs of individual and corporate clients, and these procedures are rather expensive (Aduda and Kingoo 110). In this context, the less expensive transaction is the automated clearing house payment and the most expensive transaction is the bank-teller-initiated payment that is almost equal in costs to the paper-based operations (VanHoose 423; see fig. 1).
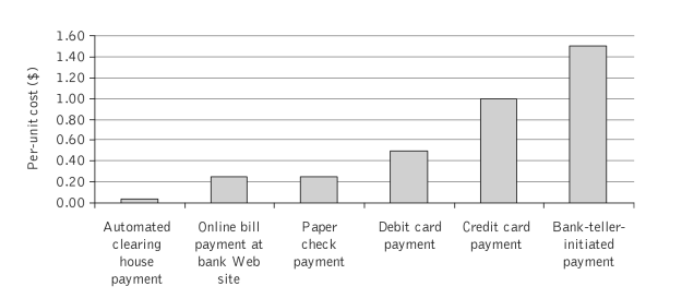
Time-Efficiency and Benefits for Clients
Electronic payment systems provide depository institutors with the possibility to serve their customers quickly and in the most efficient manner while proposing online banking services and immediate transfers. According to Hasan, Schmiedel, and Song, both bankers and clients prefer electronic payment systems for their time-efficiency and possibilities to complete operations within few minutes, hours, and only few days (Hasan, Schmiedel, and Song 166). Users of banking services note that the most convenient procedures include operations with debit and credit cards provided by MasterCard and VisaCard; online banking operations; and operations with automated teller machines (ATM) actively used in the United States of America (Wali, Wright, and Reynolds 19).
The Increased Competitiveness
Nowadays, the most popular electronic payment systems utilized by depository institutions are Clearing House Interbank Payment System (CHIPS), Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunications (SWIFT), and Eurogiro (including the European, Asian, and African countries) among others. Harris, Guru, and Avvari note that in spite of the active development of these systems, focuses on innovations, and their integration in depository institutions, the limited number of organizations and banks take the leading positions in this sphere (Harris, Guru, and Avvari 230). The reputation of banks significantly depends on the number and quality of electronic payment systems they use, and this factor influences the competitiveness (Chin and Ahmad 8).
Diversity of Provided Services
The integration of new electronic payment systems in the sphere of banking allows depository institutions to diversify the proposed services in order to attract more clients and make their experiences positive. According to AL-Adwan, AL-Zyood, and Ishfaq, today it is possible to check the accounts status online, to pay bills electronically, to make operations with the clients’ accounts online, to buy and sell stocks, to conduct operations associated with electronic transfer funds, and to use credit, debit, and smart cards among other services (AL-Adwan, AL-Zyood, and Ishfaq 16). In addition, Hasan, Schmiedel, and Song state that such diversified services as the electronic transfer funds are most important for improving the process of transferring money between depository institutions, and the opportunity for online banking and using credit and debit cards are most attractive options for clients (Hasan, Schmiedel, and Song 164).
Distant and Online Banking
Electronic funds transfers are usually used by businessmen and employees who need to receive the access to their accounts in different countries. These persons usually use the electronic data interchange services and the electronic terminals and automated teller machines (ATM) for making payments electronically or for receiving the paper currency (Chin and Ahmad 8). Other clients of depository institutions prefer the online banking when it is possible to make all such daily banking operations as paying bills online without visiting the office of the depository institution (VanHoose 424).
The Use of E-Currency
E-currency is a comparably new phenomenon in the sphere of electronic payment systems. On the one hand, as it is noted by Wali, Wright, and Reynolds, the use of e-currency can be discussed as an alternative variant to the use of traditional bank accounts because clients have electronic wallets like Skrill and such systems as PayPal (Wali, Wright, and Reynolds 18). On the other hand, the security of such operations is often guaranteed only with references to the banks that support these organizations and allow the withdrawal of money (Aduda and Kingoo 110).
The Issues of Security and Privacy
Although the use of electronic payment systems provides a lot of benefits for clients of depository institutions, they often ignore opportunities to use these methods because of the frequent cases of violating the clients’ confidentiality, privacy, and security of accounts. Omariba, Masese, and Wanyembi note that depository institutions need to resolve many cases of violation the confidentiality of personal and financial data of clients because of using electronic payment systems (Omariba, Masese, and Wanyembi 435). As a result, the level of trust for these services decreases, and customers can choose traditional banking operations or other depository institution, with the higher level of control regarding the unauthorized access to the private data (AL-Adwan, AL-Zyood, and Ishfaq 16). Another problem is the appearance of more regulations to control the privacy and security issues that are oriented to protect clients of depository institutions, but they can limit the functioning of these organizations (Harris, Guru, and Avvari 228).
The citizens of the United States and European countries can be discussed as the first bank clients who valued the use of electronic payment systems, and today these systems become actively integrated in depository institutions markets of developing countries. In spite of the fact that there is the evidence to state that electronic payment systems are appropriate to be used for the immediate online financial exchange and that such systems influence the progress of the depository institutions markets, there are still issues that can have the negative impact on the market scope. On the one hand, electronic payment systems are effective alternatives to the traditional banking procedures, and they allow clients sent and receive money easily, for instance, with the help of SWIFT transfers (Wali, Wright, and Reynolds 19). These systems also allow the time-efficient online banking or the active use of cards and terminals for non-cash operations. Moreover, such operations as cross-border payments are mostly performed with the help of electronic payment systems. Such approaches are followed in large national and international depository institutions like Bank of America (VanHoose 420). Thus, there is a tendency of widening the scope of using electronic payment systems in depository institutions, and the main focus is on developing innovative tools that can attract more customers and decrease the level of their resistance to the use of electronic resources for banking.
On the other hand, such issues as privacy and security still remain influential to prevent many bank clients from using the advantages of electronic payment systems. While comparing the situations in the United States, in the European countries, and in developing countries, it is possible to state that these issues are more taken into account by customers in developing countries, and they prefer to choose the traditional ways to work with their accounts (Stinneford, Brown, and Davis 631). In addition, the level of the customers’ trust regarding the depository institutions’ operations decreased significantly after the financial crisis of 2008, and clients of banks in the developed countries began to use the electronic money and proposed financial services rarer (Chin and Ahmad 6; Harris, Guru, and Avvari 228). However, the situation tends to change with the focus on new alternative and time-efficient operations proposed in depository institutions.
Thus, the impact of electronic payment systems on the development of the depository institutions market can be discussed as significant because the other paper-based systems are viewed as expensive, rather slow, inflexible, and requiring significant human resources. The majority of researchers and practitioners are inclined to determine more positive effects of using the electronic systems on banks (AL-Adwan, AL-Zyood, and Ishfaq 15; Harris, Guru, and Avvari 228; Omariba, Masese, and Wanyembi 433). The reason is that such systems are necessary to provide clients with more services and improve the functioning of depository institutions while enhancing the development of the national and international banking industries and markets. The only problem is in the inefficiency of certain systems to protect their customers from violating their privacy and security rights. In order to increase the customers’ trust for depository institutions that use the electronic payment systems actively, it is necessary to integrate the most reputable systems that focus on securing the electronic or online banking transactions.
The majority of depository institutions in the United States and the European countries use the electronic payment systems. Clients usually use these systems to complete electronic fund transfers with the help of such systems as CHIPS, SWIFT, and Eurogiro; to complete online transactions; to use debit, credit, and smart cards; to withdraw the e-currency from the electronic wallet; to pay bills electronically; and to use the ATM and terminals. In developing countries, the integration of electronic payment systems as alternative ones to the paper-based systems is only in the process of development. However, it is possible to observe the tendency of increasing the scope for using electronic payment systems in the national and international depository institutions markets because of a range of benefits proposed with these systems. Summarizing the benefits of integrating innovative electronic payment systems, it is important to pay attention to the cost-efficiency, time-efficiency, customer satisfaction, successful competitiveness within the market, diversity of services, possibilities for online banking and work with e-currency. Nevertheless, the development of these systems can also affect the depository institutions negatively because there are many cases when customers’ accounts and transactions cannot be secured as well as their private or confidential information.
As a result, only a few organizations like PayPal, CHIPS, SWIFT, and other similar companies dominate the international depository institutions market in terms of providing services associated with the electronic payment transactions. In this case, the market can develop further mostly in relation to proposing more services and secure environments for customers. The progress of leading electronic payment systems is important to increase the financial flows in depository institutions and serve a larger number of clients. Therefore, it is possible to state that the currently used electronic payment systems have the significant impact on the banking industry, and the progress of depository institutions depends on how effectively these systems will develop to address security and privacy issues and to serve more customers’ needs.
Aduda, Josiah, and Nancy Kingoo. “The Relationship between Electronic Banking and Financial Performance among Commercial Banks in Kenya.” Journal of Finance and Investment Analysis 1.3 (2012): 99-118. Print.
AL-Adwan, Minwer, Mahmoud AL-Zyood, and Mohammad Ishfaq. “The Impact of Electronic Payment on Saudi Banks Profitability: Case Study of SADAD Payment System.” International Journal of Research and Reviews in Applied Science 1.2 (2013): 14-21. Print.
Chin, Lai Poey and Zainal Arffin Ahmad. “Consumers’ Intention to use a Single Platform E-Payment System: A Study among Malaysian Internet and Mobile Banking Users.” Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce 20.1 (2015): 1-15. Print.
Harris, Hezlin, Balachander Krishnan Guru, and Mohan Avvari. “Evidence of Firms’ Perceptions toward Electronic Payment Systems (EPS) in Malaysia.” International Journal of Business and Information 6.2 (2011): 226-245. Print.
Hasan, Iftekhar, Heiko Schmiedel, and Liang Song. “Returns to Retail Banking and Payments.” Journal of Financial Services Research 41.3 (2012): 163-195. Print.
Omariba, Zachary, Nelson Masese, and Gail Wanyembi. “Security and Privacy of Electronic Banking.” International Journal of Computer Science Issues 9.4 (2012): 432-446. Print.
Stinneford, Ryan, Laura Hobson Brown, and Candace Modlin Davis. “Current Developments in Bank Deposits and Payment Systems.” The Business Lawyer 65.2 (2010): 629-643. Print.
VanHoose, David. E-Commerce Economics . New York: Taylor & Francis, 2011. Print.
Wali, Andy Fred, Len Tiu Wright, and Paul Reynolds. “Cashless System, Users’ Perception and Retail Marketing Performance.” International Journal of Sales, Retailing and Marketing 3.4 (2014): 17-32. Print.
- Boeing Australia Limited Current Procurement Processes
- Internet Contracts Overview and Analysis
- Ballistics Evidence of John F. Kennedy's Assassination
- Monetary Policy in the United States
- Policies in Canada to Enhance Economics
- Storefront Project for Souk E-Gift Shop
- Management Information Systems: Primis Online System at McGraw Hill
- Computer Sciences Technology: E-Commerce
- Global Business Strategy: Telecommunication
- How E-Business Enhance Business Performance: B2B, B2C, C2C
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, April 16). Electronic Payment Systems: Advantages and Disadvantages. https://ivypanda.com/essays/electronic-payment-systems-advantages-and-disadvantages/
"Electronic Payment Systems: Advantages and Disadvantages." IvyPanda , 16 Apr. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/electronic-payment-systems-advantages-and-disadvantages/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Electronic Payment Systems: Advantages and Disadvantages'. 16 April.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Electronic Payment Systems: Advantages and Disadvantages." April 16, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/electronic-payment-systems-advantages-and-disadvantages/.
1. IvyPanda . "Electronic Payment Systems: Advantages and Disadvantages." April 16, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/electronic-payment-systems-advantages-and-disadvantages/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Electronic Payment Systems: Advantages and Disadvantages." April 16, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/electronic-payment-systems-advantages-and-disadvantages/.
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The following are the advantages and disadvantages of Digital Payment: Advantages of Digital Payment. Convenience – Digital payments offer a high level of convenience, allowing users to make purchases from the comfort of their own home or on the go.
E-payments enhance and entice consumers and customers to shift to digital modes of payment. Hence, it helps in the digitalization of the economy. Disadvantages of Digital Payment. Security. E-payments are prone to cybercriminals who disable online payments and exploit them to steal such people’s money.
Explore the pros and cons of digital payment systems with our comprehensive guide. Discover the seven advantages and disadvantages that come with the convenience of modern-day digital transactions.
Find out the advantages and disadvantages of Digital payment enabled by several applications (banking/wallets).
Explore the advantages and disadvantages of online payments in this insightful guide. Learn how they can impact your business efficiency, security, and customer satisfaction.
Table of Content. What is an Electronic Payment System? Types of Electronic Payment System. Advantages of Electronic Payment System. Disadvantages of Electronic Payment System. Regulatory Bodies Governing Electronic Payment System in India. Regulations Relating to Electronic Payment System. Conclusion. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Check here for Essay on Digital Banking with includes Pros & Cons useful for Descriptive Paper writing for Mains Exams 2019.
This article examines the movement towards a digital economy and using digital payments from multiple perspectives. Considering that digital models and paradigms are the much discussed and debated topics at the moment, this article breaks down the what, why, how, and if aspects of the digital economy.
The purpose of this paper is to examine the existing literature on the problem, analyze the electronic payment systems’ benefits and limitations, and evaluate the overall impact of the systems’ integration on the development of depository institutions markets.
With the rise of e-commerce and mobile technology, more and more people are turning to virtual payments as a convenient and secure way to make transactions. However, as with any payment method, there are both advantages and disadvantages to virtual payments that should be carefully considered.