Appointments at Mayo Clinic
- Pregnancy week by week
- Fetal presentation before birth
The way a baby is positioned in the uterus just before birth can have a big effect on labor and delivery. This positioning is called fetal presentation.
Babies twist, stretch and tumble quite a bit during pregnancy. Before labor starts, however, they usually come to rest in a way that allows them to be delivered through the birth canal headfirst. This position is called cephalic presentation. But there are other ways a baby may settle just before labor begins.
Following are some of the possible ways a baby may be positioned at the end of pregnancy.

Head down, face down
When a baby is head down, face down, the medical term for it is the cephalic occiput anterior position. This the most common position for a baby to be born in. With the face down and turned slightly to the side, the smallest part of the baby's head leads the way through the birth canal. It is the easiest way for a baby to be born.
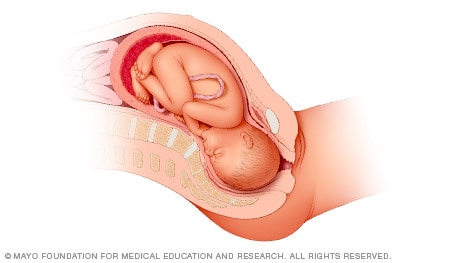
Head down, face up
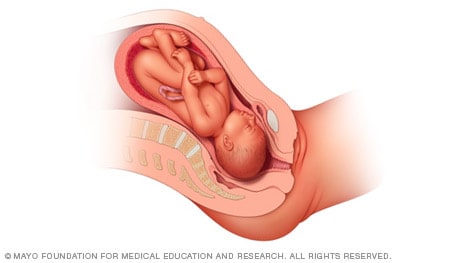
When a baby is head down, face up, the medical term for it is the cephalic occiput posterior position. In this position, it might be harder for a baby's head to go under the pubic bone during delivery. That can make labor take longer.
Most babies who begin labor in this position eventually turn to be face down. If that doesn't happen, and the second stage of labor is taking a long time, a member of the health care team may reach through the vagina to help the baby turn. This is called manual rotation.
In some cases, a baby can be born in the head-down, face-up position. Use of forceps or a vacuum device to help with delivery is more common when a baby is in this position than in the head-down, face-down position. In some cases, a C-section delivery may be needed.
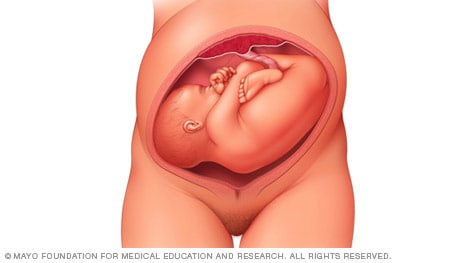
Frank breech
When a baby's feet or buttocks are in place to come out first during birth, it's called a breech presentation. This happens in about 3% to 4% of babies close to the time of birth. The baby shown below is in a frank breech presentation. That's when the knees aren't bent, and the feet are close to the baby's head. This is the most common type of breech presentation.
If you are more than 36 weeks into your pregnancy and your baby is in a frank breech presentation, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. It involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a breech position, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Most babies in a frank breech position are born by planned C-section.

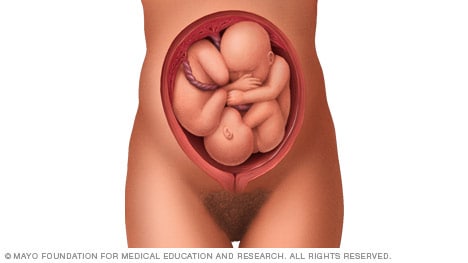
Complete and incomplete breech
A complete breech presentation, as shown below, is when the baby has both knees bent and both legs pulled close to the body. In an incomplete breech, one or both of the legs are not pulled close to the body, and one or both of the feet or knees are below the baby's buttocks. If a baby is in either of these positions, you might feel kicking in the lower part of your belly.
If you are more than 36 weeks into your pregnancy and your baby is in a complete or incomplete breech presentation, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. It involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a breech position, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Many babies in a complete or incomplete breech position are born by planned C-section.

When a baby is sideways — lying horizontal across the uterus, rather than vertical — it's called a transverse lie. In this position, the baby's back might be:
- Down, with the back facing the birth canal.
- Sideways, with one shoulder pointing toward the birth canal.
- Up, with the hands and feet facing the birth canal.
Although many babies are sideways early in pregnancy, few stay this way when labor begins.
If your baby is in a transverse lie during week 37 of your pregnancy, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. External cephalic version involves one or two members of your health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a transverse lie, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Many babies who are in a transverse lie are born by C-section.
If you're pregnant with twins and only the twin that's lower in the uterus is head down, as shown below, your health care provider may first deliver that baby vaginally.
Then, in some cases, your health care team may suggest delivering the second twin in the breech position. Or they may try to move the second twin into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. External cephalic version involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
Your health care team may suggest delivery by C-section for the second twin if:
- An attempt to deliver the baby in the breech position is not successful.
- You do not want to try to have the baby delivered vaginally in the breech position.
- An attempt to move the baby into a head-down position is not successful.
- You do not want to try to move the baby to a head-down position.
In some cases, your health care team may advise that you have both twins delivered by C-section. That might happen if the lower twin is not head down, the second twin has low or high birth weight as compared to the first twin, or if preterm labor starts.
- Landon MB, et al., eds. Normal labor and delivery. In: Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2021. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Accessed May 19, 2023.
- Holcroft Argani C, et al. Occiput posterior position. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 19, 2023.
- Frequently asked questions: If your baby is breech. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/if-your-baby-is-breech. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Hofmeyr GJ. Overview of breech presentation. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Strauss RA, et al. Transverse fetal lie. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Chasen ST, et al. Twin pregnancy: Labor and delivery. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Cohen R, et al. Is vaginal delivery of a breech second twin safe? A comparison between delivery of vertex and non-vertex second twins. The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine. 2021; doi:10.1080/14767058.2021.2005569.
- Marnach ML (expert opinion). Mayo Clinic. May 31, 2023.
Products and Services
- A Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to a Healthy Pregnancy
- 3rd trimester pregnancy
- Fetal development: The 3rd trimester
- Overdue pregnancy
- Pregnancy due date calculator
- Prenatal care: Third trimester
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- NEW: Listen to Health Matters Podcast - Mayo Clinic Press NEW: Listen to Health Matters Podcast
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
- Healthy Lifestyle
Double your impact!
Your GivingTuesday gift can go 2X as far.
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Diet & Nutrition
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
What Is Cephalic Position?
The ideal fetal position for labor and delivery
- Why It's Best
Risks of Other Positions
- Determining Position
- Turning a Fetus
The cephalic position is when a fetus is head down when it is ready to enter the birth canal. This is one of a few variations of how a fetus can rest in the womb and is considered the ideal one for labor and delivery.
About 96% of babies are born in the cephalic position. Most settle into it between the 32nd and 36th weeks of pregnancy . Your healthcare provider will monitor the fetus's position during the last weeks of gestation to ensure this has happened by week 36.
If the fetus is not in the cephalic position at that point, the provider may try to turn it. If this doesn't work, some—but not all—practitioners will attempt to deliver vaginally, while others will recommend a Cesarean (C-section).
Getty Images

Why Is the Cephalic Position Best?
During labor, contractions dilate the cervix so the fetus has adequate room to come through the birth canal. The cephalic position is the easiest and safest way for the baby to pass through the birth canal.
If the fetus is in a noncephalic position, delivery becomes more challenging. Different fetal positions have a range of difficulties and varying risks.
A small percentage of babies present in noncephalic positions. This can pose risks both to the fetus and the mother, and make labor and delivery more challenging. It can also influence the way in which someone can deliver.
A fetus may actually find itself in any of these positions throughout pregnancy, as the move about the uterus. But as they grow, there will be less room to tumble around and they will settle into a final position.
It is at this point that noncephalic positions can pose significant risks.
Cephalic Posterior
A fetus may also present in an occiput or cephalic posterior position. This means they are positioned head down, but they are facing the abdomen instead of the back.
This position is also nicknamed "sunny-side up."
Presenting this way increases the chance of a painful and prolonged delivery.
There are three different types of breech fetal positioning:
- Frank breech: The legs are up with the feet near the head.
- Footling breech: One or both legs is lowered over the cervix.
- Complete breech: The fetus is bottom-first with knees bent.
A vaginal delivery is most times a safe way to deliver. But with breech positions, a vaginal delivery can be complicated.
When a baby is born in the breech position, the largest part—its head—is delivered last. This can result in them getting stuck in the birth canal (entrapped). This can cause injury or death.
The umbilical cord may also be damaged or slide down into the mouth of the womb, which can reduce or cut off the baby's oxygen supply.
Some providers are still comfortable performing a vaginal birth as long as the fetus is doing well. But breech is always a riskier delivery position compared with the cephalic position, and most cases require a C-section.
Likelihood of a Breech Baby
You are more likely to have a breech baby if you:
- Go into early labor before you're full term
- Have an abnormally shaped uterus, fibroids , or too much amniotic fluid
- Are pregnant with multiples
- Have placenta previa (when the placenta covers the cervix)
Transverse Lie
In transverse lie position, the fetus is presenting sideways across the uterus rather than vertically. They may be:
- Down, with the back facing the birth canal
- With one shoulder pointing toward the birth canal
- Up, with the hands and feet facing the birth canal
If a transverse lie is not corrected before labor, a C-section will be required. This is typically the case.
Determining Fetal Position
Your healthcare provider can determine if your baby is in cephalic presentation by performing a physical exam and ultrasound.
In the final weeks of pregnancy, your healthcare provider will feel your lower abdomen with their hands to assess the positioning of the baby. This includes where the head, back, and buttocks lie
If your healthcare provider senses that the fetus is in a breech position, they can use ultrasound to confirm their suspicion.
Turning a Fetus So They Are in Cephalic Position
External cephalic version (ECV) is a common, noninvasive procedure to turn a breech baby into cephalic position while it's still in the uterus.
This is only considered if a healthcare provider monitors presentation progress in the last trimester and notices that a fetus is maintaining a noncephalic position as your delivery date approaches.
External Cephalic Version (ECV)
ECV involves the healthcare provider applying pressure to your stomach to turn the fetus from the outside. They will attempt to rotate the head forward or backward and lift the buttocks in an upward position. Sometimes, they use ultrasound to help guide the process.
The best time to perform ECV is about 37 weeks of pregnancy. Afterward, the fetal heart rate will be monitored to make sure it’s within normal levels. You should be able to go home after having ECV done.
ECV has a 50% to 60% success rate. However, even if it does work, there is still a chance the fetus will return to the breech position before birth.
Natural Methods For Turning a Fetus
There are also natural methods that can help turn a fetus into cephalic position. There is no medical research that confirms their efficacy, however.
- Changing your position: Sometimes a fetus will move when you get into certain positions. Two specific movements that your provider may recommend include: Getting on your hands and knees and gently rocking back and forth. Another you could try is pushing your hips up in the air while laying on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor (bridge pose).
- Playing stimulating sounds: Fetuses gravitate to sound. You may be successful at luring a fetus out of breech position by playing music or a recording of your voice near your lower abdomen.
- Chiropractic care: A chiropractor can try the Webster technique. This is a specific chiropractic analysis and adjustment which enables chiropractors to establish balance in the pregnant person's pelvis and reduce undue stress to the uterus and supporting ligaments.
- Acupuncture: This is a considerably safe way someone can try to turn a fetus. Some practitioners incorporate moxibustion—the burning of dried mugwort on certain areas of the body—because they believe it will enhance the chances of success.
A Word From Verywell
While most babies are born in cephalic position at delivery, this is not always the case. And while some fetuses can be turned, others may be more stubborn.
This may affect your labor and delivery wishes. Try to remember that having a healthy baby, and staying well yourself, are your ultimate priorities. That may mean diverting from your best laid plans.
Speaking to your healthcare provider about turning options and the safest route of delivery may help you adjust to this twist and feel better about how you will move ahead.
Glezerman M. Planned vaginal breech delivery: current status and the need to reconsider . Expert Rev Obstet Gynecol. 2012;7(2):159-166. doi:10.1586/eog.12.2
Cleveland Clinic. Fetal positions for birth .
MedlinePlus. Breech birth .
UT Southwestern Medical Center. Can you turn a breech baby around?
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. If your baby is breech .
Roecker CB. Breech repositioning unresponsive to Webster technique: coexistence of oligohydramnios . Journal of Chiropractic Medicine . 2013;12(2):74-78. doi:10.1016/j.jcm.2013.06.003
By Cherie Berkley, MS Berkley is a journalist with a certification in global health from Johns Hopkins University and a master's degree in journalism.

IMAGES