Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts

Research articles
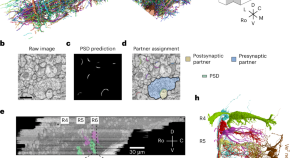
Predicting modular functions and neural coding of behavior from a synaptic wiring diagram
The authors determine the synaptic wiring diagram of a vertebrate circuit and reveal behaviorally associated modules. A model based on this connectome predicts neural coding and dynamics that are verified with calcium imaging data.
- Ashwin Vishwanathan
- Sarah Williams
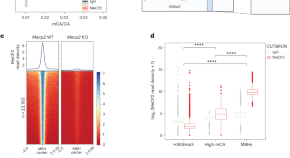
Interaction of methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2) with distinct enhancers in the mouse cortex
The Rett syndrome protein MeCP2 regulates gene transcription by binding to methylated DNA. Here the authors find that MeCP2 also regulates key neuronal genes by binding to nonmethylated DNA, providing new insights into the disorder.
- Gyan Prakash Mishra
- Eric X. Sun
- Hume Stroud
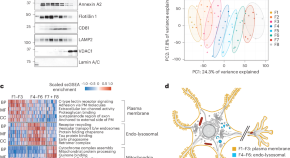
Tau filaments are tethered within brain extracellular vesicles in Alzheimer’s disease
Using cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) and proteomics, this study identifies the tethering of pathological tau filaments within defined brain extracellular vesicles in Alzheimer’s disease, shining light on the link between these vesicles and tau pathology.
- Stephanie L. Fowler
- Tiana S. Behr
- Benjamin Ryskeldi-Falcon
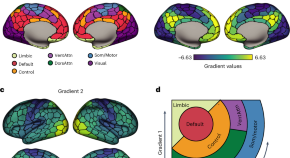
The cell-type underpinnings of the human functional cortical connectome
Here Zhang et al. establish multiscale relationships that link postmortem cell-type distributions with the in vivo functional organization of the human cerebral cortex, as assessed through functional magnetic resonance imaging.
- Xi-Han Zhang
- Kevin M. Anderson
- Avram J. Holmes
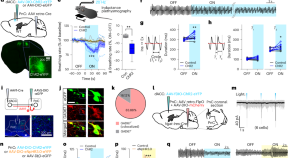
A top-down slow breathing circuit that alleviates negative affect in mice
Jhang et al. identify a prefrontal–pontomedullary pathway that slows breathing and reduces anxiety in mice, where the pontine reticular nucleus converts excitatory prefrontal inputs into inhibitory signals to brainstem respiratory networks.
- Jinho Jhang
- Seahyung Park
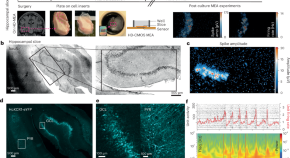
Multimodal evaluation of network activity and optogenetic interventions in human hippocampal slices
Brain slices offer an experimental window into human neurophysiology. Using high-density microelectrode array recordings and adeno-associated virus–mediated optogenetics, the authors demonstrate that optogenetic targeting of CAMK2A+ neurons can affect network activity in human hippocampal slices.
- John P. Andrews
- Jinghui Geng
- Tomasz Jan Nowakowski
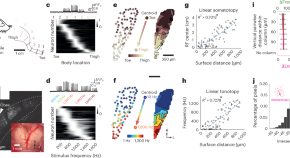
Emergence of a brainstem somatosensory tonotopic map for substrate vibration
Lee et al. show that the development of the somatotopic map and the tonotopic map for substrate vibration is shaped by the intrinsic distribution of cutaneous end organs and selective dendritic integration within the brainstem dorsal column nuclei.
- Kuo-Sheng Lee
- Alastair J. Loutit
- Daniel Huber
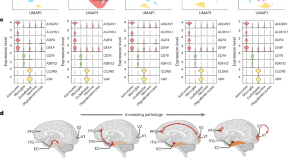
Astrocyte transcriptomic changes along the spatiotemporal progression of Alzheimer’s disease
Using single-nucleus RNA sequencing from 32 donors, researchers identified distinct astrocytic gene expression programs activated across brain regions and Alzheimer’s disease stages. They also found unique subclusters of astrocytes that appear to vary over time, highlighting the complexity of astrocytic responses in AD.
- Alberto Serrano-Pozo
- Sudeshna Das
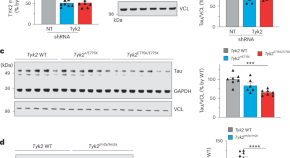
TYK2 regulates tau levels, phosphorylation and aggregation in a tauopathy mouse model
Tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) critically regulates tau levels and aggregation by phosphorylating tau’s tyrosine 29. Partial inhibition of TYK2 mitigates tau pathologies in cells and mice, highlighting TYK2 as a potential therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies.
- Bakhos Tadros
- Huda Yahya Zoghbi
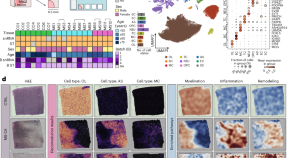
Cell type mapping reveals tissue niches and interactions in subcortical multiple sclerosis lesions
Lerma-Martin et al. generated a paired single-nucleus RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics dataset from subcortical multiple sclerosis lesions, identifying spatial niches and key cell interactions driving inflammation and disease progression at the lesion rim.
- Celia Lerma-Martin
- Pau Badia-i-Mompel
- Lucas Schirmer
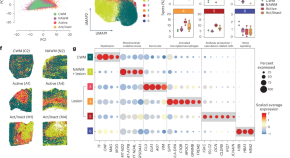

Spatially resolved gene signatures of white matter lesion progression in multiple sclerosis
Lesion initiation and progression in multiple sclerosis is a dynamic but unclear process. Here, the authors highlight cell type-specific gene sets characterizing the action lesion rims and identify trajectories, predicting how normal-appearing white matter can develop into active and mixed active/inactive lesions.
- Astrid M. Alsema
- Marion H. C. Wijering
- Bart J. L. Eggen
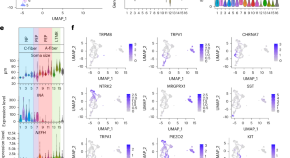
Leveraging deep single-soma RNA sequencing to explore the neural basis of human somatosensation
Dorsal root ganglia (DRGs) contain a plethora of neuron types. The authors show that the existence of human-specific DRG neuronal types and microneurography recordings reveal distinct temperature-sensing properties across human sensory afferent types.
- Huasheng Yu
- Saad S. Nagi
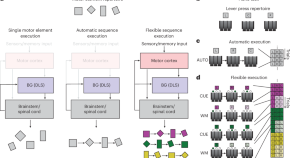
The role of motor cortex in motor sequence execution depends on demands for flexibility
Motor cortex is required for flexible motor sequences informed by sensory cues but not for single automatic sequences. However, training automatic sequences alongside flexible ones interferes with their subcortical consolidation.
- Kevin G. C. Mizes
- Jack Lindsey
- Bence P. Ölveczky
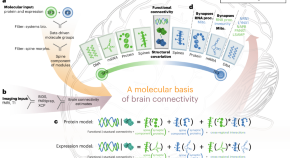
Integration across biophysical scales identifies molecular and cellular correlates of person-to-person variability in human brain connectivity
Integration of postmortem molecular and dendritic spine morphological measurements enables the detection of microscale molecules associated with person-to-person variability in macroscale brain connectivity estimated from antemortem neuroimaging.
- Shinya Tasaki
- Jeremy H. Herskowitz
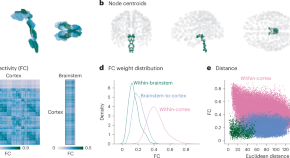
Integrating brainstem and cortical functional architectures
Hansen et al. used in vivo functional imaging of the human brainstem and cortex to demonstrate how the brainstem shapes cortical functional architecture, including oscillatory dynamics, cognitive specialization and hierarchical organization.
- Justine Y. Hansen
- Simone Cauzzo
- Bratislav Misic
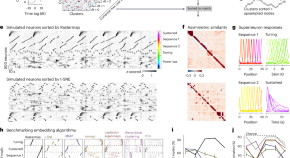
Rastermap: a discovery method for neural population recordings
Rastermap is an analysis method for exploring dynamical and spatial relationships among hundreds to hundreds of thousands of neurons. The algorithm uses a fast optimization technique to discover complex neural patterns, such as sequences.
- Carsen Stringer
- Marius Pachitariu
A cross-disease resource of living human microglia identifies disease-enriched subsets and tool compounds recapitulating microglial states
Profiling >200,000 live human microglia from 74 donors across neurological diseases reveals 12 subtypes of microglia that were validated in situ. Camptothecin is also identified as a compound reducing disease-enriched microglial subsets.
- John F. Tuddenham
- Mariko Taga
- Philip L. De Jager
The hippocampal CA2 region discriminates social threat from social safety
The hippocampal dorsal CA2 enables the recognition of novel conspecifics. Kassraian et al. show that it is also required for discriminating safety- versus threat-associated conspecifics and that its disruption gives rise to generalized social avoidance.
- Pegah Kassraian
- Shivani K. Bigler
- Steven A. Siegelbaum

Integrated multimodal cell atlas of Alzheimer’s disease
The affected cellular populations during Alzheimer’s disease progression remain understudied. Here the authors use a cohort of 84 donors, quantitative neuropathology and multimodal datasets from the BRAIN Initiative. Their pseudoprogression analysis revealed two disease phases.
- Mariano I. Gabitto
- Kyle J. Travaglini
Modeling Parkinson’s disease pathology in human dopaminergic neurons by sequential exposure to α-synuclein fibrils and proinflammatory cytokines
Bayati et al. discovered that sequential treatment of iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons with α-synuclein fibrils and proinflammatory cytokines leads to the formation of Lewy body–like inclusions, through the downregulation of lysosomal proteins.
- Armin Bayati
- Riham Ayoubi
- Peter S. McPherson
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO